7. C, E models#
7.1. Characteristics of the models#
The models are above all a test of DYNA_NON_LINE with keyword SCHEMA_TEMPS (FORMULATION =” ACCELERATION “), whose results are compared with DYNA_NON_LINE with keyword SCHEMA_TEMPS (FORMULATION =” DEPLACEMENT”).
The mass-spring systems are modelled, as in modeling A, by a discrete element with 3 degrees of freedom DIS_T. Only modeling with one degree of freedom is tested.
Problem modeling:
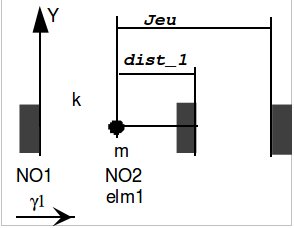
Figure 7.1-a : Modeling of a mass-spring system impacting a rigid wall
Node \(\mathrm{NO1}\) is subject to an imposed acceleration \({\gamma }_{1}(t)\). We calculate the relative displacement of node \(\mathrm{NO2}\), its training displacement, and its absolute displacement.
An element of type DIST_T on a POI1 mesh is used to simulate the impact of the beam on a rigid wall: any impacts between the beam and the obstacle are taken into account as being forces internal to this element. It is assigned a non-linear shock-type behavior (DIS_CHOC for modeling C and DIS_CONTACT for modeling E) via the definition of the characteristics DIS_CONTACT of the command DEFI_MATERIAU.
The thickness of material surrounding the shock node in the direction in question is specified by the operand DIST_1 of the DEFI_MATERIAU command. In the case treated, we choose DIST_1 \(=0.4495\) and JEU \(=0.45\) so that at the initial moment, the shock node and the obstacle are separated from the game \(j=5.{10}^{-4}\mathrm{mm}\) (cf. figure).
The seismic load, due to the imposed movements of node \(\mathrm{NO1}\), is calculated by the operator CALC_CHAR_SEISME. A charge concept is then created from the VECT_ASSE operand of the AFFE_CHAR_MECA command.
We use the explicit NEWMARK integration diagram of the DIFFERENCES CENTREES type with a time step of \({10}^{-3}s\). The calculation by DYNA_NON_LINE with keyword SCHEMA_TEMPS (FORMULATION =” ACCELERATION “) is performed in the modal space, the non-linearity being due to the shock and therefore remaining local.
7.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
The mesh associated with the model consists of 2 nodes, a SEG2 mesh of type DIS_T and a point mesh POI1 of type DIS_T.