9. G modeling#
9.1. Characteristics of modeling#
It is the same modeling as the E model, but in \(\mathrm{3D}\). The junctions are constructed in the same way.
9.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
The mesh, identical to that of modeling C, is represented in FIG. 5.2-a.
9.3. Tested sizes and results#
The quantities tested are identical to those presented for modeling E. Tests on DZ are added.
Identification |
Reference |
tolerance |
0.07 |
|
DEPZON_1 |
DX- \({\mathrm{Depl}}_{X}\) |
MIN |
0 |
|
MAX |
0 |
0.07 |
||
DY- \({\mathrm{Depl}}_{Y}\) |
MIN |
0 |
0.07 |
|
MAX |
0 |
0.07 |
||
DEPZON_2 |
DX- \({\mathrm{Depl}}_{X}\) |
MIN |
0 |
0.07 |
MAX |
0 |
0.07 |
||
DY- \({\mathrm{Depl}}_{Y}\) |
MIN |
0 |
0.07 |
|
MAX |
0 |
0.07 |
||
DEPZON_3 |
DX- \({\mathrm{Depl}}_{X}\) |
MIN |
0 |
0.07 |
MAX |
0 |
0.07 |
||
DY- \({\mathrm{Depl}}_{Y}\) |
MIN |
0 |
0.07 |
|
MAX |
0 |
0.07 |
||
DEPZON_4 |
DX- \({\mathrm{Depl}}_{X}\) |
MIN |
0 |
0.07 |
MAX |
0 |
0.07 |
||
DY- \({\mathrm{Depl}}_{Y}\) |
MIN |
0 |
0.07 |
|
MAX |
0 |
0.07 |
||
Table 9.3-1
The deformation is shown in Figure 9.4-a.
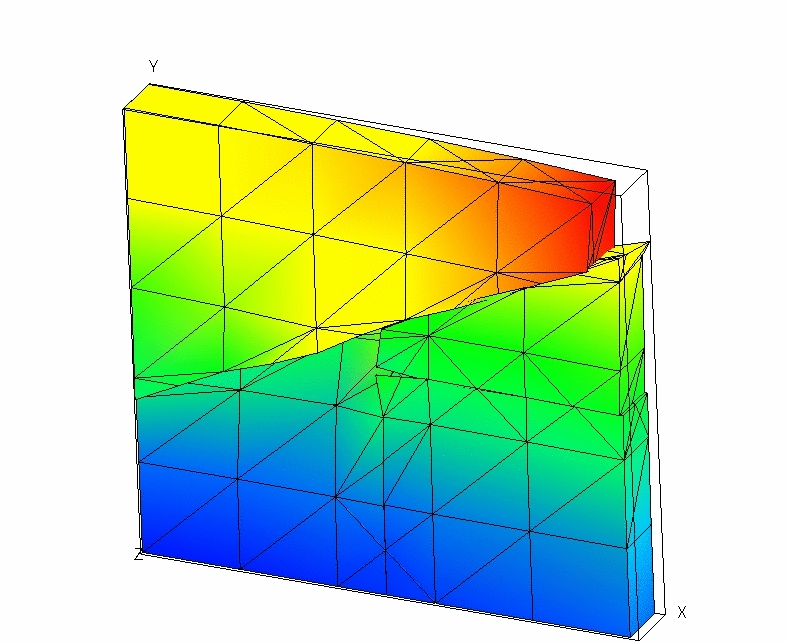
Figure 9.4-a: Deformed structure (Exaggeration 10).
9.4. notes#
The remarks are identical to those formulated for modeling E.