4. B modeling#
4.1. Characteristics of modeling#
In this modeling, the crack is not meshed (case X- FEM).
In order to obtain better precision on the results, the initial free mesh was refined at the crack bottom using the MACR_ADAP_MAIL command.
Figure 4.1-1: Refined structure mesh
4.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
Number of knots: 1146
Number of meshes and type: 64573 TETRA4
The characteristic length of an element near the crack bottom is \(\mathrm{0,07}m\).
4.3. Tested sizes and results#
The choice of numerical parameters for post-processing SIFs is identical to that made for modeling A.
In addition, in order to smooth the results of CALC_G_XFEM (unavoidable on a free mesh), it is necessary to post-treat SIFs only at a limited number of points, distributed uniformly along the crack bottom. Here 21 post-treatment points are selected (initially, there are 289 points along the crack bottom). It also reduces post-processing time CPU.
In the same way, 21 post-processing points are chosen for POST_K1_K2_K3.
4.3.1. Values from CALC_G#
The values are in \(\mathit{Pa}\mathrm{.}\sqrt{m}\).
Identification |
Reference Type |
Reference Value |
% Tolerance |
\(\mathit{max}({K}_{I})\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
7,978 105 |
|
\(\mathit{min}({K}_{I})\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
7,978 105 |
|
\({K}_{\mathit{II}}\) in \(\omega \mathrm{=}0°\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
9,386 105 |
|
\({K}_{\mathit{III}}\) in \(\omega \mathrm{=}90°\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
6,570 105 |
|
4.3.2. Values from POST_K1_K2_K3#
The values are in \(\mathit{Pa}\mathrm{.}\sqrt{m}\).
Identification |
Reference Type |
Reference Value |
% Tolerance |
\(\mathit{max}({K}_{I})\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
7,978 105 |
|
\(\mathit{min}({K}_{I})\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
7,978 105 |
|
\({K}_{\mathit{II}}\) in \(\omega \mathrm{=}0°\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
9,386 105 |
|
\({K}_{\mathit{III}}\) in \(\omega \mathrm{=}90°\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
6,570 105 |
|
4.4. notes#
It can be seen that, as for modeling A, CALC_K_G_XFEM gives less accurate results than POST_K1_K2_K3. For curved fronts, it is better to prefer the post-treatment of SIF with POST_K1_K2_K3, to maintain an acceptable error in propagating a crack. The X- FEM results are as accurate as the results with a mesh crack (modeling A), which further reinforces the value of using X- FEM compared to the FEM method.
A very good agreement is obtained between the values of K2 and K3 calculated with POST_K1_K2_K3 and the values of the analytical solution (see).
In addition, no interference effect is observed at the edges, as is the case in modeling A. With a meshed crack, we in fact note the appearance of shear at the through points of the crack that is difficult to explain (see).
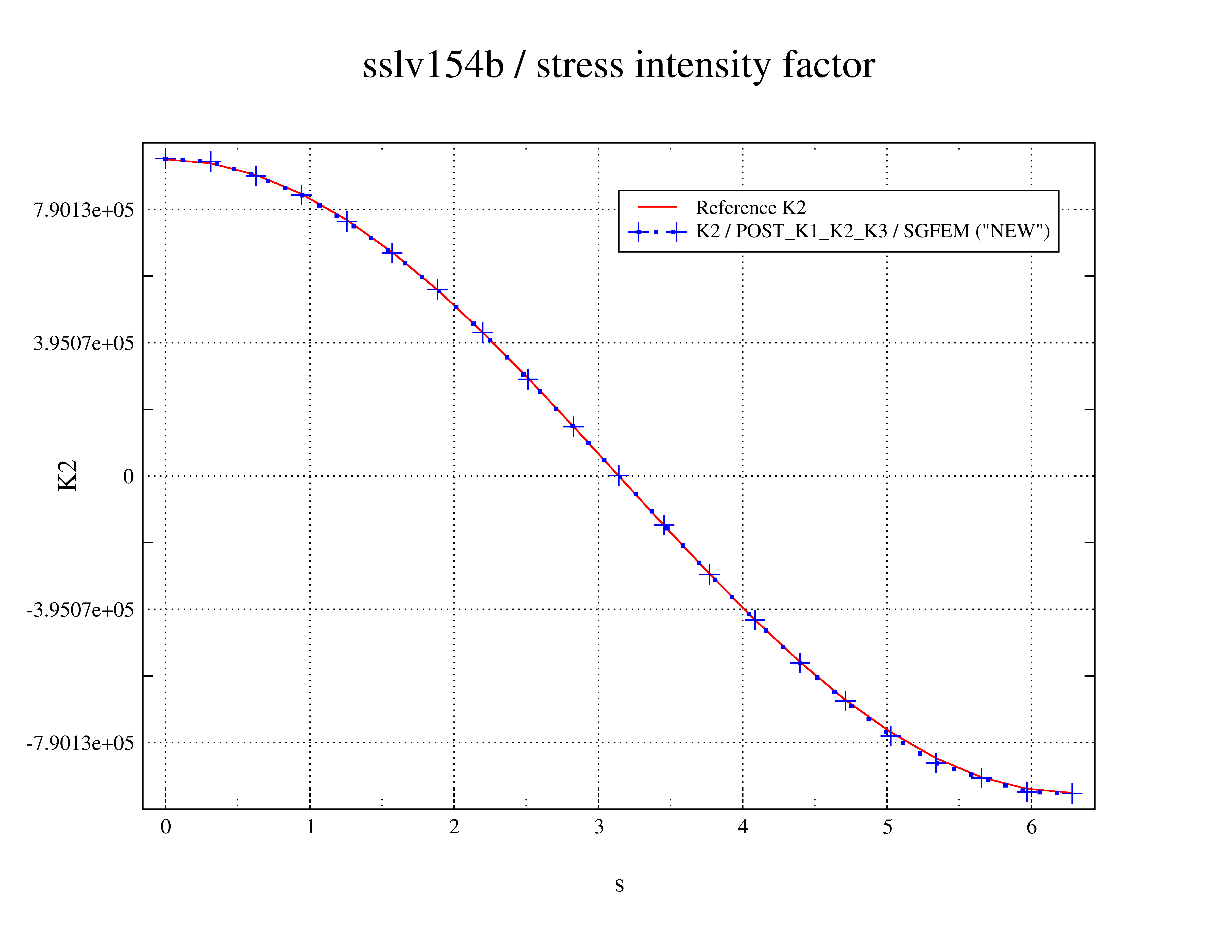
Figure 4.4-1: mode 2 along the forehead as a function of the curvilinear abscissa
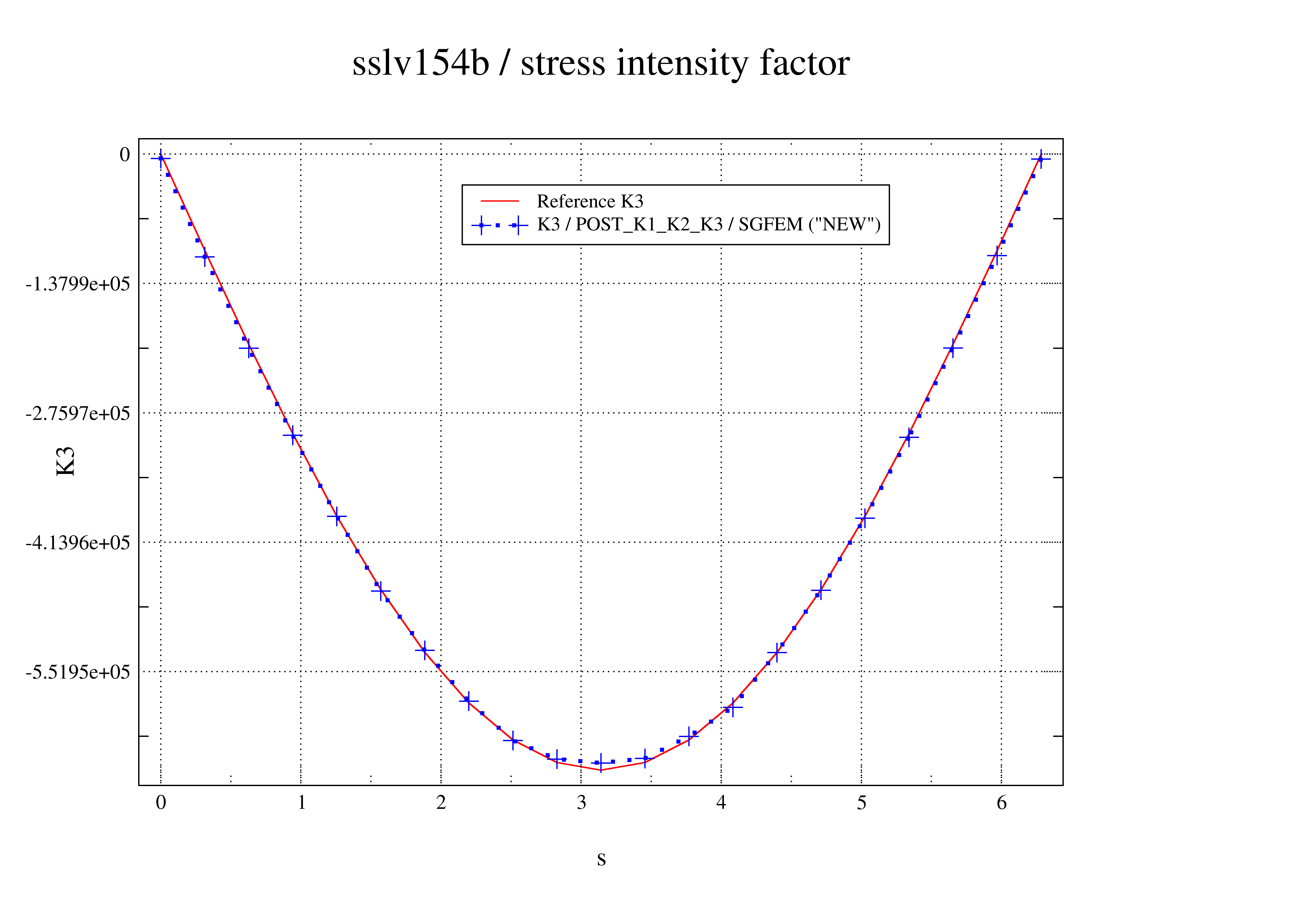
Figure 4.4-2: mode 3 along the forehead as a function of the curvilinear abscissa