6. D modeling#
6.1. Characteristics of modeling#
We use a AXIS model (linear elements).
The continuous contact formulation is used.
6.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
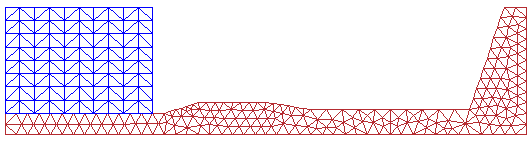
Number of knots: 333
Number of meshes: 510 TRIA3 and 152 SEG2
Number of nodes in contact: 20
6.3. Tested sizes and results#
The following displacement \(Y\) of the point \(K\) of the piece of paper with respect to the surface \(\mathrm{ABCDEFG}\) of the die is tested.
Identification |
Reference type |
Reference value |
Tolerance |
Point \(K\)/Point \(B\) - \(\mathrm{DY}\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
5.0000 |
|
Point \(K\)/Point \(C\) - \(\mathrm{DY}\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
20.8250 |
|
Point \(K\)/Point \(D\) - \(\mathrm{DY}\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
55.8800 |
|
Point \(K\)/Point \(E\) - \(\mathrm{DY}\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
78.6900 |
|
Point \(K\)/Point \(F\) - \(\mathrm{DY}\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
144.8950 |
|
Point \(K\)/Point \(G\) - \(\mathrm{DY}\) |
“ANALYTIQUE” |
155.0960 |
|
We test the number of iterations of Newton when the point \(K\) of the plot is in front of the points \(B\), \(C\), \(D\), \(E\), \(F\) and \(G\) of the string.
Identification |
Reference type |
Reference value |
Tolerance |
ITER_GLOB/Point \(B\) |
“NON_REGRESSION” |
1 |
0.00% |
ITER_GLOB/Point \(C\) |
“NON_REGRESSION” |
1 |
0.00% |
ITER_GLOB/Point \(D\) |
“NON_REGRESSION” |
1 |
0.00% |
ITER_GLOB/Point \(E\) |
“NON_REGRESSION” |
1 |
0.00% |
ITER_GLOB/Point \(F\) |
“NON_REGRESSION” |
1 |
0.00% |
ITER_GLOB/Point \(G\) |
“NON_REGRESSION” |
1 |
0.00% |
We test the state of the contact (field CONT_NOEU) when the point \(K\) of the piece is in front of the points between \(E\) and \(F\) and all the \(\mathrm{5mm}\).
Identification |
Reference type |
Reference value |
Tolerance |
CONT/Point \(E\) |
“NON_REGRESSION” |
0 |
|
CONT/Point \(E\) + \(\mathrm{5mm}\) |
“NON_REGRESSION” |
0 |
|
CONT/Point \(E\) + \(\mathrm{10mm}\) |
“NON_REGRESSION” |
2 |
|
CONT/Point \(E\) + \(\mathrm{15mm}\) |
“NON_REGRESSION” |
2 |
|
CONT/Point \(F\) |
“NON_REGRESSION” |
2 |
|
The first two points are not in contact. |
6.4. notes#
The calculation is carried out by imposing a displacement on the back side of the block \(\text{(MN)}\). The displacement is imposed in the following way:
|
\(\mathrm{0.mm}\) to |
\(\mathrm{5.mm}\) in 5 steps |
|
\(\mathrm{5.mm}\) to |
\(\mathrm{20.mm}\) in 5 steps |
|
\(\mathrm{20.mm}\) to |
\(\mathrm{50.mm}\) in 5 steps |
|
\(\mathrm{50.mm}\) to |
\(\mathrm{70.mm}\) in 5 steps |
|
\(\mathrm{70.mm}\) to |
\(\mathrm{140.mm}\) in 5 steps |
|
\(\mathrm{140.mm}\) to |
\(\mathrm{155.mm}\) in 5 steps |
The calculations do not converge with the default keywords used for convergence in STAT_NON_LINE, because the default value of RESI_GLOB_RELA = 1.E-6 is too restrictive (the forces to which the piece is subjected are initially relatively weak). To overcome this problem, use the keyword RESI_GLOB_MAXI = 1.E-6.