1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
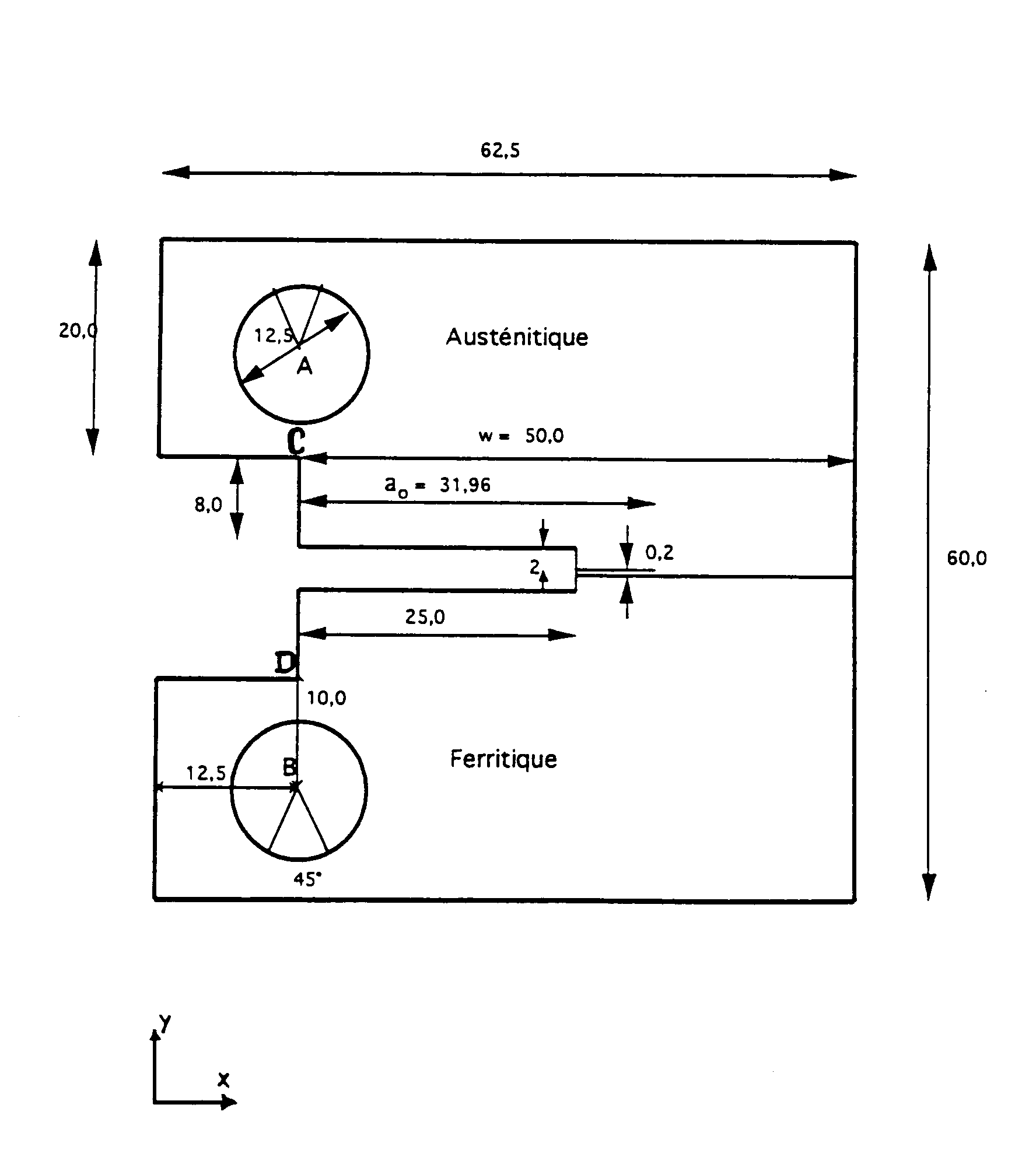
All ratings are in \(\mathrm{mm}\). The crack is located \(\mathrm{0,2}\mathrm{mm}\) from the interface, in the upper part of the specimen.
1.2. Material properties#
Material #1: austenitic steel
Von Mises elastoplastic with isotropic work hardening
Young’s modulus \({E}_{1}\mathrm{=}{2.10}^{5}\mathit{MPa}\), Poisson’s ratio \({\nu }_{1}=\mathrm{0,3}\)
Elastic limit \({\sigma }_{\mathit{y1}}\mathrm{=}310\mathit{MPa}\)
Uniaxial tensile curve:
\(\sigma (\mathrm{MPa})\) |
0 |
310 |
310 |
600 |
700 |
\(\varepsilon\) |
0 |
0.155 |
0.155 |
40 |
100 |
Material #2: ferritic steel
Von Mises elastoplastic with isotropic work hardening
Young’s modulus \({E}_{2}={2.10}^{5}\mathrm{MPa}\), Poisson’s ratio \({\nu }_{2}=\mathrm{0,3}\)
Elastic limit \({\sigma }_{\mathrm{y2}}=442\mathrm{MPa}\)
\(\sigma (\mathrm{MPa})\) |
0 |
442 |
442 |
600 |
650 |
\(\varepsilon\) |
0 |
0.221 |
40 |
100 |
Material #3: almost non-deformable pins
Isotropic linear elastic
Young’s modulus \({E}_{3}={6.10}^{10}\mathrm{MPa}\), Poisson’s ratio \({\nu }_{3}=\mathrm{0,3}\)
1.3. Boundary conditions and loading#
Given the asymmetry of the materials, the entire specimen is modelled.
Blocks:
\(\mathrm{UX}=\mathrm{UY}=0\) |
at point \(B\) (center of the lower pin) |
\(\mathrm{UX}=0\) |
at point \(A\) (center of the top pin) |
Loading per imposed displacement:
: label: EQ-None
0lemathrm {UY}le 1mathrm {mm}
The load is therefore monotonous and increasing.