1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
The structure is modelled in plane deformations.
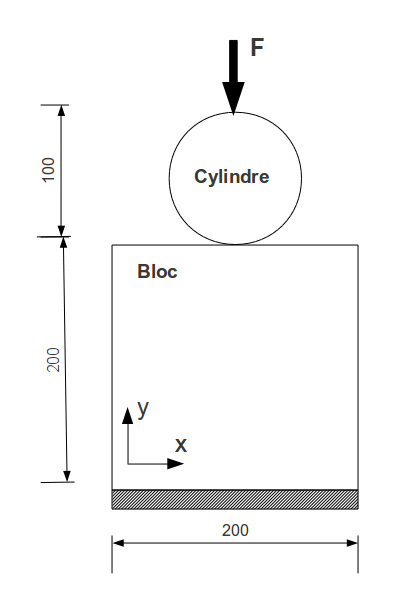
Note \(B\) the point on the upper side of the block belonging to the plane of symmetry.
1.2. Material properties#
Block:
Poisson’s ratio: \(\mathrm{0,3}\)
Young’s module: \(70000{\mathit{N.mm}}^{-2}\)
Cylinder:
Poisson’s ratio: \(\mathrm{0,3}\)
Young’s module: \(210000{\mathit{N.mm}}^{-2}\)
The coefficient of friction between the block and the cylinder is \(\mu =\mathrm{0,1}\) .
1.3. Boundary conditions and loads#
Since the structure is symmetric and subjected to a loading that respects symmetry, only one half is shown. We therefore apply \(\mathit{DX}=0\) on the plane of symmetry.
The block is embedded at its base:
\(\mathit{DX}=0\)
\(\mathit{DY}=0\)
The cylinder is subjected to a point force at its top:
\(\mathit{FY}=35\mathit{kN}\), which is \(\mathit{FY}=17500N\) for the semi-structure