7. F modeling#
7.1. Characteristics of F modeling#
The characteristics of the modeling are strictly identical to the modeling \(E\). Only the mesh differs.
7.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
An entirely triangular mesh of the plate is produced, which does not conform to the crack, such that certain intersected edges are non-vital.
Volume elements (\(\mathrm{DCB}\)): 842 TRI3
7.3. Tested sizes and results#
The start of the calculation requires a few more subdivisions than modeling \(E\). Given this difference in subdivision sequences, the results of models \(E\) and \(F\) are slightly different compared moment by moment. On the other hand, we can see in the figure that they are superposable. Having proved this correspondence, we therefore take the non-regression reference value as the reference value for non-regression those from modeling \(F\).
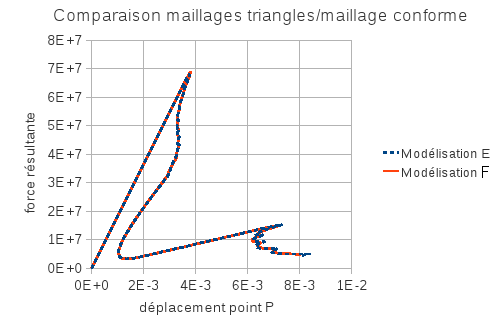
Figure 7.3-a : Comparison of triangle meshes/conformal mesh
Size tested |
Reference type |
Code_Aster |
Tolerance ( \(\text{\%}\) )) ** |
\(U\) at time 50 |
|
3.34481D-03 |
0.10 |
\(F\) at time 50 |
|
4.26501D+07 |
0.10 |
\(U\) at time 100 |
|
2.28519D-03 |
0.10 |
\(F\) at time 100 |
|
4.85041D+06 |
0.10 |
\(U\) at the moment 150 |
|
6.83775D-03 |
0.10 |
\(F\) at the moment 150 |
|
6.86061D+06 |
0.10 |