5. D modeling#
5.1. Characteristics of modeling D#
The simulation of the propagation of cracks by brittle fracture is carried out with modeling PLAN_JOINT and the law of behavior CZM_EXP_REG for cohesive meshes. The solid elements, in plane deformations D_ PLAN, are elastic.
5.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
A linear unstructured mesh of the perforated half-plate and of the potential crack is produced.
Volume elements (DCB): 804 TRIA3
Joint elements (crack path): 19 QUAD4
5.3. Tested sizes and results#
Non-regression tests are performed on the overall response: \({F}^{i}\) resulting from the force imposed on the upper face versus \(U\) displacement of the node \(P\) at the top of the hole.
We can see that the criminalization of cohesive law introduces a slight difference between the results. If we compare the results of modeling D to those of B in this way, we have the force-displacement curve of the figure.
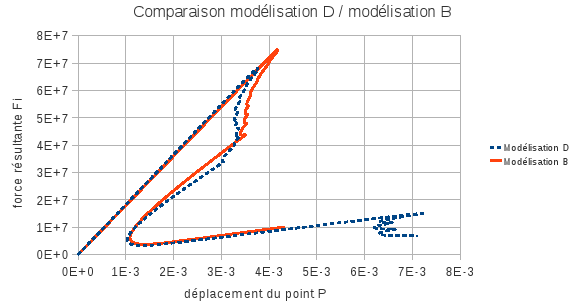
Figure 5.3-a : comparison of joint elements with elements with internal discontinuity.