4. C modeling#
4.1. Characteristics of modeling#
A modeling testing the functionalities of contact with friction treated with the continuous method has been implemented. Given the symmetry of the problem, it comprises a quarter of the ring as well as the mesh of a non-deformable plate.
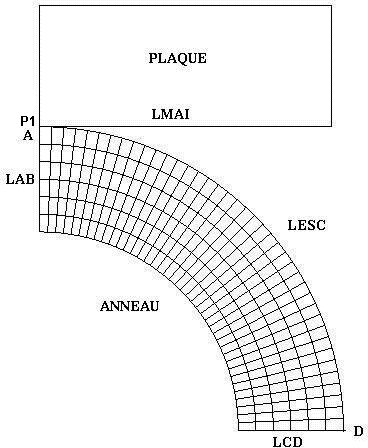
Boundary condition:
Symmetry conditions: |
the nodes of group \(\mathrm{LAB}\) located in the plane \(X=0\) are blocked in the direction \(X\) (\(\mathrm{DX}=0\)), the nodes of the group \(\mathrm{LCD}\) located in the plane \(Y=0\) are blocked in the direction \(Y\) (\(\mathrm{DY}=0\)), all the nodes in mesh group \(«\mathrm{Plaque}»\) are blocked in the direction \(X\) (\(\mathrm{DX}=0\)) |
To avoid rigid body movements, nodes \(A\) and \(\mathrm{P1}\) have the same vertical displacement.
Loads:
Imposed displacement following \(Y\) on all nodes of the plate: \(\mathrm{DY}\) varies from \(0\) to \(\mathrm{2,225}\mathrm{cm}\).
(the value of \(\mathrm{4,45}\mathrm{cm}\) is the vertical approximation of the two symmetric plates).
Note:
The mesh was made in \(\mathrm{cm}\) .
4.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
The mesh is identical in every way to the mesh used for B modeling.
4.3. Tested sizes and results#
4.4. note#
The results are very similar to those of B modeling.