1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
We consider a cube with side \(\mathrm{2L}\) and a lens-shaped crack with radius \(R\) such as \(\frac{L}{R}\mathrm{=}5\) and central angle \(\alpha \mathrm{=}\frac{\pi }{4}\) (see).
The equation characteristic of the shape of the crack surface is:
\({x}^{2}+{y}^{2}+{(z\mathrm{-}R)}^{2}\mathrm{=}{R}^{2}\) with \(0\mathrm{\le }z\mathrm{\le }(1\mathrm{-}\mathrm{cos}\alpha )R\).
We pose \(a\mathrm{=}R\mathrm{sin}\alpha\).
1.2. The characteristic equation of the crack background is:#
\({x}^{2}+{y}^{2}\mathrm{=}{a}^{2}\) with \(z\mathrm{=}(1\mathrm{-}\mathrm{cos}\alpha )R\)
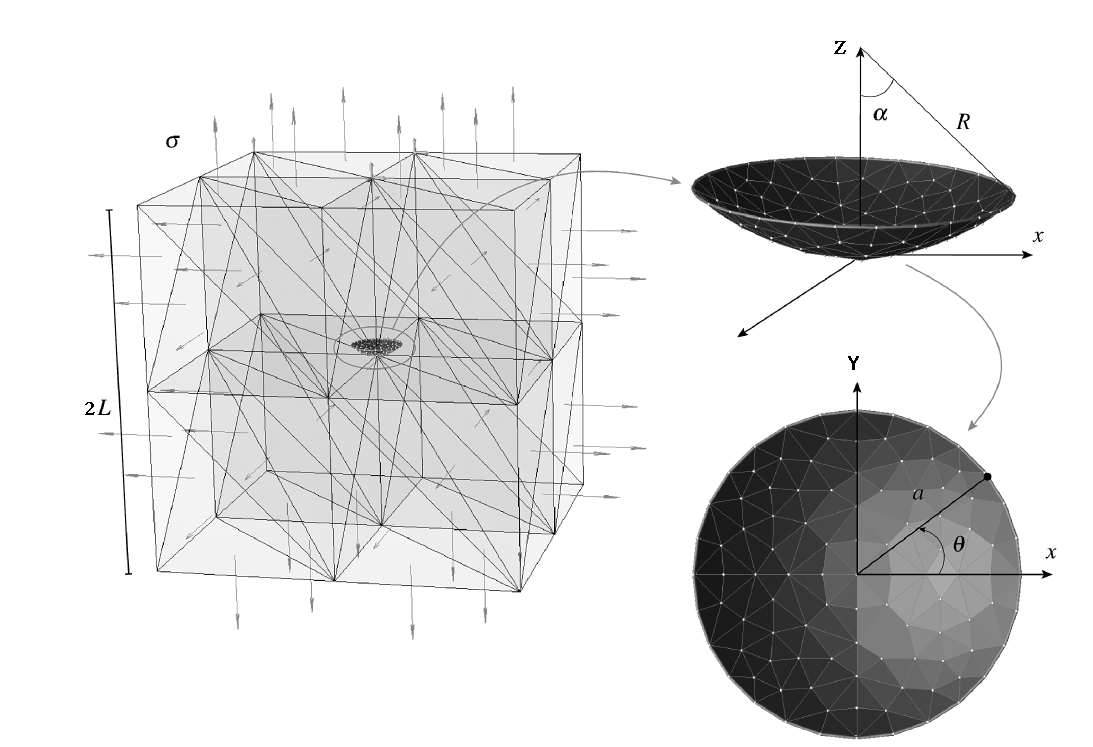
Figure 1: geometry of the cracked cube
1.3. Material properties#
The material is elastic isotropic in properties:
\(E\mathrm{=}210000\mathit{MPa}\)
\(\mathrm{\nu }=\mathrm{0,22}\)
1.4. Boundary conditions and loads#
The cube is subjected to hydrostatic tension \(\sigma\).