1. Reference problem#
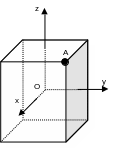
1.1. Geometry#
Cube geometry:
Center \(O(0.\mathrm{,0}\mathrm{.}\mathrm{,0}\mathrm{.})\)
Point \(A(0.5\mathrm{,0}.5\mathrm{,0}.5)\)
Side cube \(1m\)
1.2. Material properties#
Elastic
\(E=5800.0\mathrm{E6}\mathrm{Pa}\) Young’s module
\(\rho =2500{\mathrm{kg.m}}^{-3}\) Density
\(\nu =0.3\) Poisson’s ratio
DRUCK_PRAGER with linear negative work hardening
\(\alpha =0.33\) Pressure Dependence Coefficient
\({p}_{\mathrm{ultm}}=0.01\) Ultimate cumulative plastic deformation
\({\sigma }^{Y}=2.57\mathrm{E6}\mathrm{Pa}\) Plastic constraint
\(h=-2.00\mathrm{E8}\mathrm{Pa}\) Work hardening module
DRUCK_PRAGER with parabolic negative work hardening
\(\mathrm{\alpha }=0.33\) Pressure Dependence Coefficient
\({p}_{\mathit{ultm}}=0.01\) Ultimate cumulative plastic deformation
\({\mathrm{\sigma }}^{Y}=2.57E6\mathit{Pa}\) Plastic constraint
\({\mathrm{\sigma }}_{\mathit{ultm}}^{Y}=0.57E6\mathit{Pa}\) Ultimate constraint
DRUCK_PRAG_N_A with parabolic negative work hardening
\(\alpha =0.33\) Pressure Dependence Coefficient
\({p}_{\mathrm{ultm}}=0.01\) Ultimate cumulative plastic deformation
\({\sigma }^{Y}=2.57\mathrm{E6}\mathrm{Pa}\) Plastic constraint
\({\sigma }_{\mathrm{ultm}}^{Y}=0.57\mathrm{E6}\mathrm{Pa}\) Ultimate constraint
\(\mathrm{\beta }=0.33\) Initial expansion coefficient
Hydraulic behavior: saturated liquid
\(\mathrm{Pre1}=1\mathrm{Pa}\) Reference liquid pressure
\({\rho }_{\mathrm{pre1}}=1000{\mathrm{kg.m}}^{-3}\) Density of water
\(\mathrm{Poro}=0.14\) Initial porosity
\({\rho }_{\mathrm{vh}}=2400{\mathrm{kg.m}}^{-3}\) Homogenized density
\(\mathrm{bio}=1\) Biot coefficient
\({K}_{\mathrm{intrinsèque}}=1E-18{m}^{2}\) Intrinsic permeability
\(\frac{1}{{K}_{l}}=0\) Incompressible liquid
\(\mathrm{vi}=1.0E-3\mathrm{Pa.s}\) Viscosity
1.3. Boundary conditions and loads#
Boundary conditions and loads are applied in two steps:
Step \(A\): \(t\in [\mathrm{0,1}\mathrm{.}]\)
Boundary conditions
Knot pressure \(\mathrm{PRE1}=0.\)
Imposed movements, of symmetry, on the faces of the cube belonging to the planes
\(X=-0.5\) \(\mathrm{DX}=0\)
\(Y=-0.5\) \(\mathrm{DY}=0\)
\(Z=-0.5\) \(\mathrm{DZ}=0\)
Loading
We progressively apply \(p={2.10}^{6}\mathrm{Pa}\) compression to the faces of the cube belonging to the planes: \(X=0.5\), \(Y=0.5\) and \(Z=0.5\)
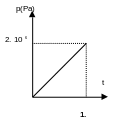
Step B: \(t\in \text{]}\mathrm{1,2}\mathrm{.}\text{]}\)
From the state of constraints obtained at instant \(t=1.s\), the following conditions are applied to the faces of the cube:
Movations
For the face belonging to plane \(Z=0.5\), the \(\mathrm{DZ}\) displacement is gradually applied, following a ramp:
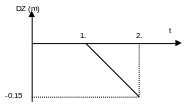
For faces belonging to planes \(X=-0.5,Y=-0.5,Z=-0.5\), symmetry conditions are applied.
Loads: the loads applied are constant:
Face belonging to plane \(X=0.5\) \(p={2.10}^{6}\mathrm{Pa}\)
Face belonging to plane \(Z=0.5\) \(p={2.10}^{6}\mathrm{Pa}\)