7. E modeling#
7.1. Characteristics of modeling#
We use a MEMBRANE modeling in large deformations (DEFORMATION =” GROT_GDEP “) with the Neo-Hookian law of behavior (RELATION =” ELAS_MEMBRANE_NH”). Quadratic elements are used.
7.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
The mesh is the same as for B modeling.
7.3. Tested sizes and results#
The pressure applied during loading is tested.
Identification |
Reference type |
Reference value |
Precision |
Instant 0.1 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
109.55 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.2 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
531.73 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.3 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
995.8 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.4 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1276.2 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.5 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1366.9 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.6 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1344.7 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.7 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1280.6 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.8 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1203.0 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.9 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1124.4 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 1.0 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1049.0 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
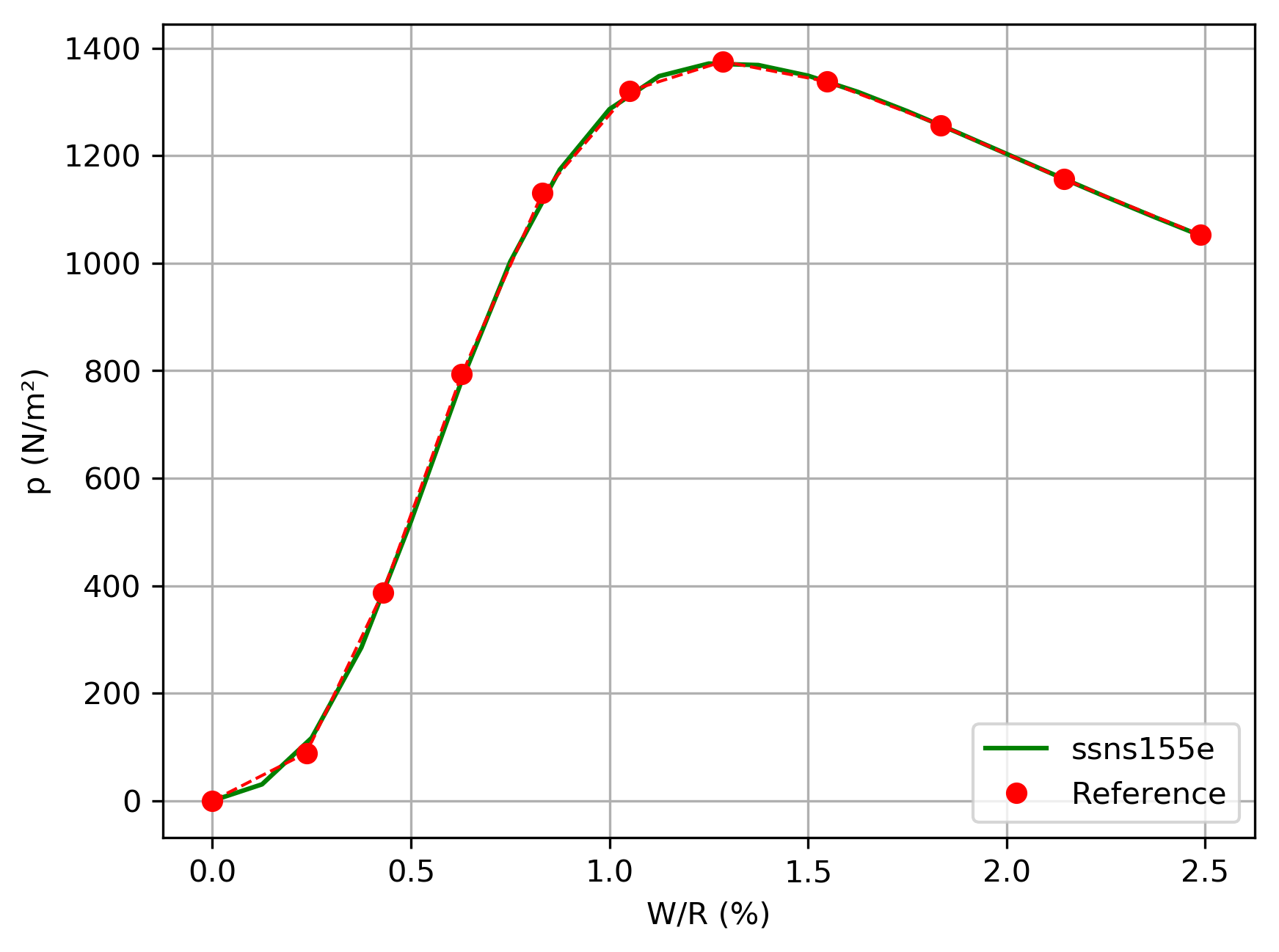
Figure 6.2 -a: Results of E modeling vs numerical reference in figure 2.1 -a.
7.4. notes#
We used on-the-go piloting (SUIV_PILO) as for the D modeling.
Unlike D-modeling, the cells are quadratic, and therefore of the same type as for the reference solution. It is noted that the results are then much more accurate compared to the reference solution, which is very satisfactory considering the fact that the mesh is approximately 2 times coarser.