6. D modeling#
6.1. Characteristics of modeling#
We use a MEMBRANE modeling in large deformations (DEFORMATION =” GROT_GDEP “) with the Neo-Hookian law of behavior (RELATION =” ELAS_MEMBRANE_NH”). Linear elements are used.
6.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
The mesh is the same as for modeling A.
6.3. Tested sizes and results#
The pressure applied during loading is tested.
Identification |
Reference type |
Reference value |
Precision |
Instant 0.1 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
109.55 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.2 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
531.73 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.3 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
995.8 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.4 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1276.2 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.5 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1366.9 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.6 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1344.7 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.7 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1280.6 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.8 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1203.0 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 0.9 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1124.4 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
Instant 1.0 - \(\mathit{ETA}\text{\_}\mathit{PILO}\) |
“SOURCE_EXTERNE” |
1049.0 \(N/{m}^{2}\) |
|
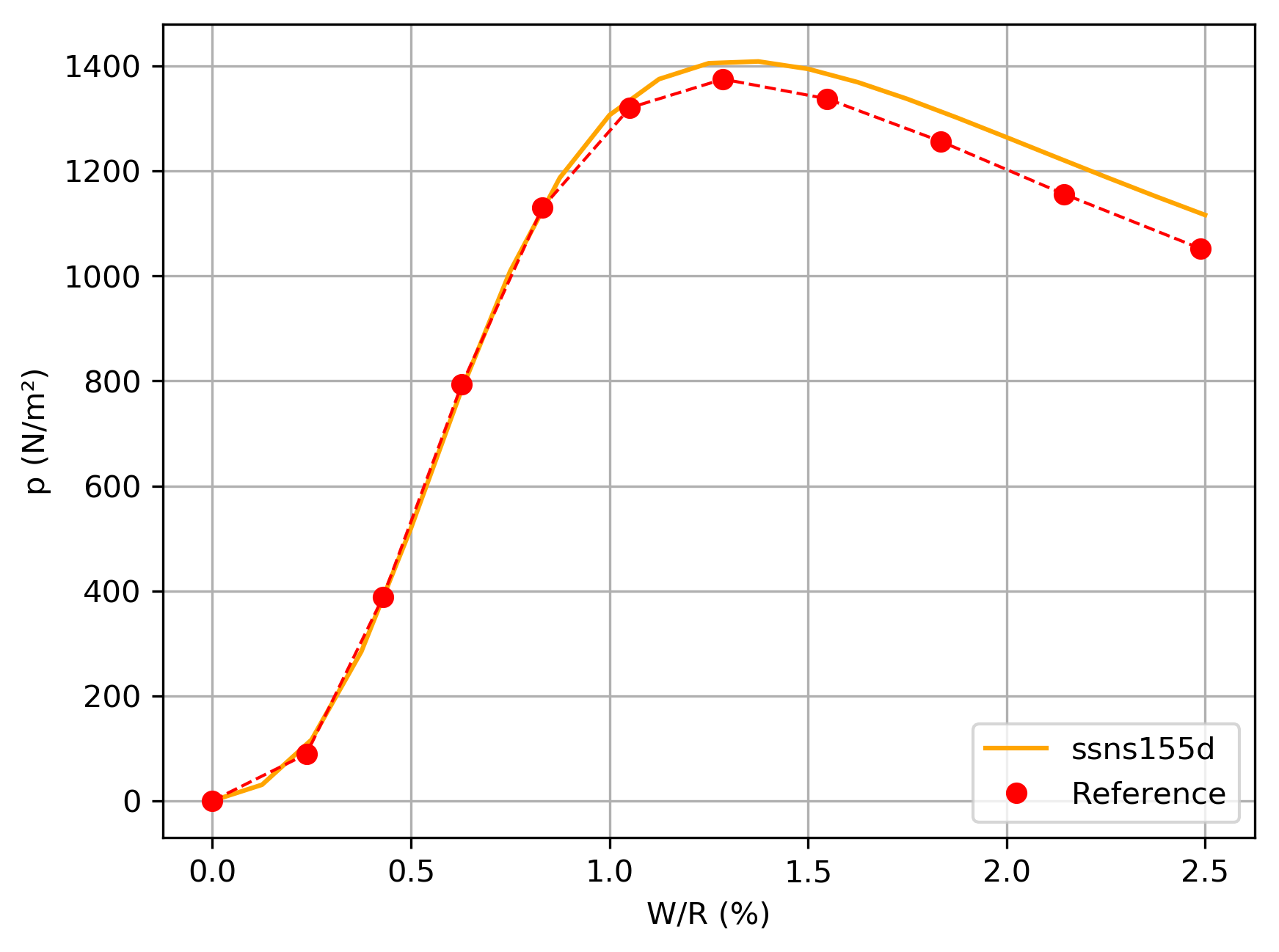
Figure 6.2-a: Results of the D modeling vs numerical reference in figure 2.1 -a.
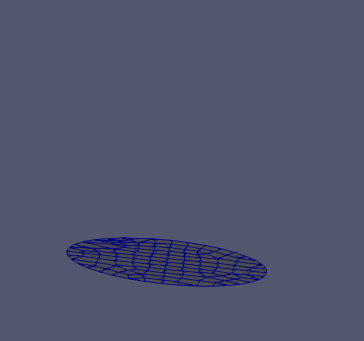
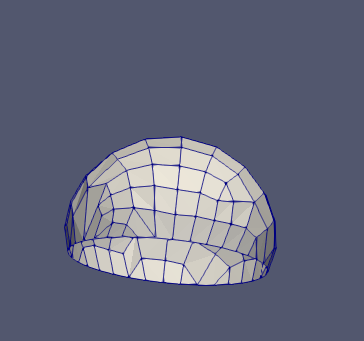
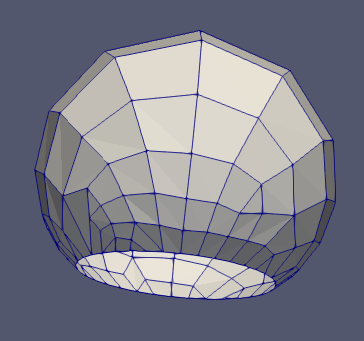
Figure 6.2-b: Initial state (left), deformed at time 0.5 (center) and deformed at final state (right).
6.4. notes#
We used on-the-go piloting (SUIV_PILO) to achieve convergence. The Neo-Hookian law of behavior reveals a snap-through at around 1.4kPa. This leads to strong non-linearities around this value that can be overcome by controlling the follower pressure.
The mesh is approximately 2 times coarser than that of the reference and the meshes are linear and not quadratic. This explains the differences observed compared to the reference solution for this modeling.