3. Modeling A#
3.1. Characteristics of modeling#
MEC3QU9H (degenerate 3D shell)
modeling COQUE_3D - regular mesh.
3.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
Number of knots: 33
Number of meshes and type: 10 QUAD9
3.3. Tested features#
The geometric nonlinear element COQUE_3D,
The static algorithm for updating large rotations GROT_GDEP from STAT_NON_LINE,
The use of a follower pressure.
3.4. Results of modeling A#
History of horizontal displacement \(\mathit{DX}\) (\(m\)) in the middle of \(\mathit{P1P2}\)
Moment |
Press \(p\) |
Reference (Samcef) |
—9.03743E+00 |
||
—1.41513E+01 |
Story of vertical displacement \(\mathit{DZ}\) (m) in the middle of \(\mathit{P1P2}\)
Moment |
Press \(P\) |
Reference (Samcef) |
—8.42753E+00 |
||
—4.43375E+00 |
History of the horizontal rotation \(\mathit{DRY}\) in the middle of \(\mathit{P1P2}\)
Moment |
Press \(p\) |
Reference (Samcef) |
1.94328E+00 |
||
3.09814E+00 |
3.5. notes#
The number of cells in the reference solution is 2 times greater than that of the modeling A solution.
We use the value of COEF_RIGI_DRZ = 0.001.
The following figures illustrate the solution obtained with a non-follower and follower pressure. These are the translation components of the middle of the free end.
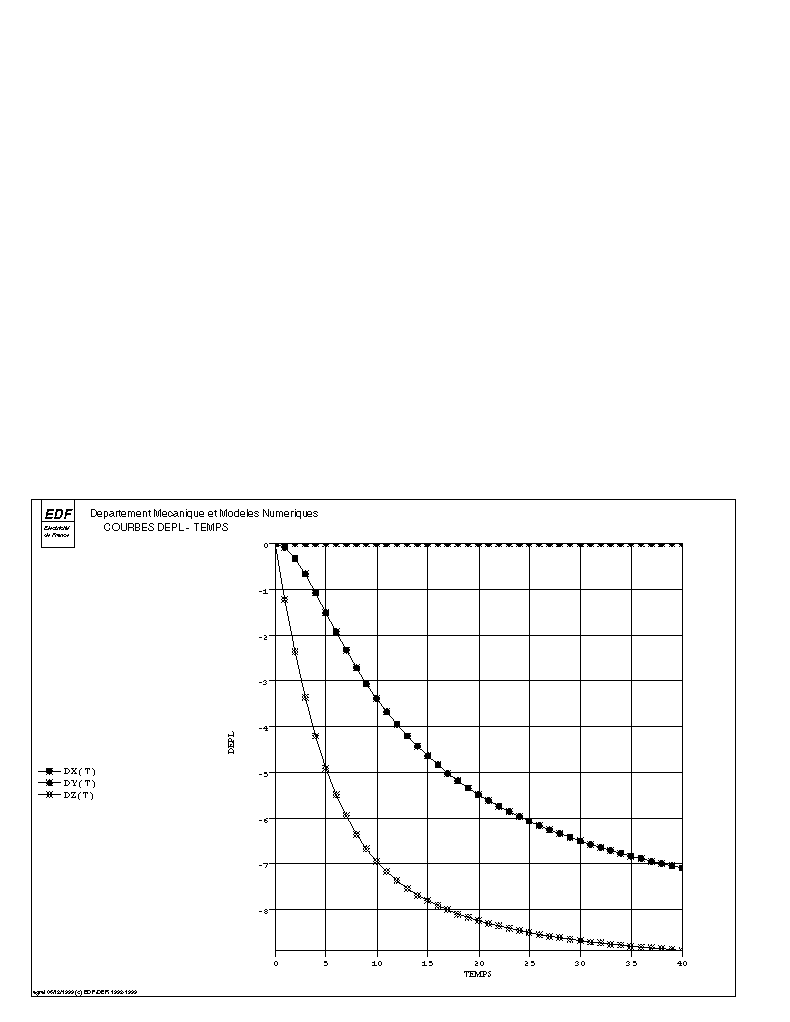
Non-tracking pressure |
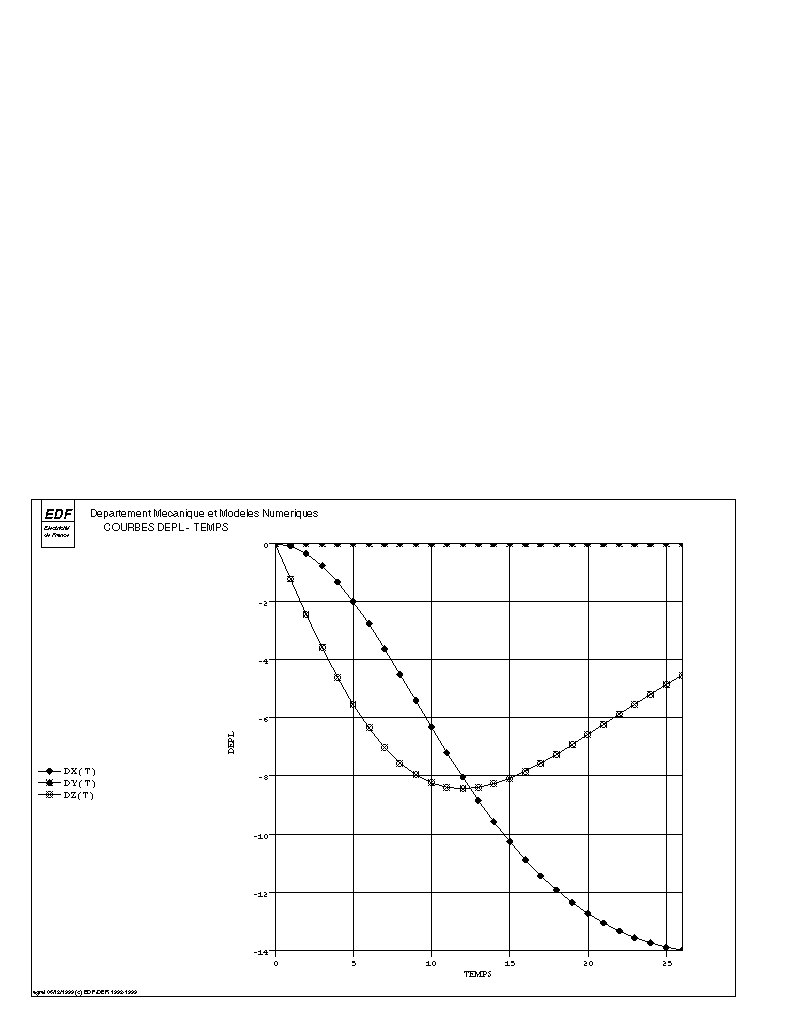
Follower pressure |
We can see that in the case of a subsequent pressure, the displacement \(\mathit{DZ}\) decreases after reaching a maximum. The beam has a tendency to roll up. This phenomenon cannot be represented with unsteady pressures.