3. Modeling A#
3.1. Characteristics of modeling#
The slope is modelled in D_ PLAN.
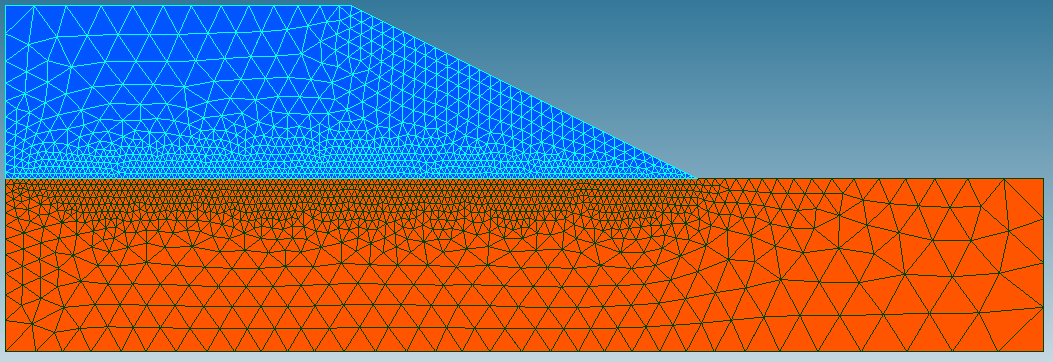
The slope mesh with foundation is shown in fig4-modeleA.
The mesh composed of quadratic triangular elements is refined around the intersection between the slope and the foundation and also on the inclined side.
We use the macro command CALC_STAB_PENTE with METHODE_STAB = “SRM” to analyze the stability of the slope at the 3 values of \(\lambda\) representing the two rupture mechanisms and the transition state. The exponential increment refinement method is used to estimate the safety factor to within 0.01.
3.2. Tested sizes and results#
We test the safety factor corresponding to the 3 values of \(\lambda\) selected. The reference values are shown in Tableau 2.
Table 2: FS reference values (Modeling A)
Identification |
Aster Result |
Reference Value |
Error |
FS (\(\lambda =\mathrm{1,0}\)) |
1.46 |
1.448 |
0.8% |
FS (\(\lambda =\mathrm{1,5}\)) |
2.03 |
2.032 |
|
FS (\(\lambda =\mathrm{4,0}\)) |
2.05 |
2.032 |
|
3.3. Summary of results#
The result of the safety factors from the macro command CALC_STAB_PENTE gives the maximum difference of 0.9% with respect to the reference solution. This proves the relevance of the result and the applicability of method SRM implemented in code_aster to the 2D model composed of an inhomogeneous material field.