1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
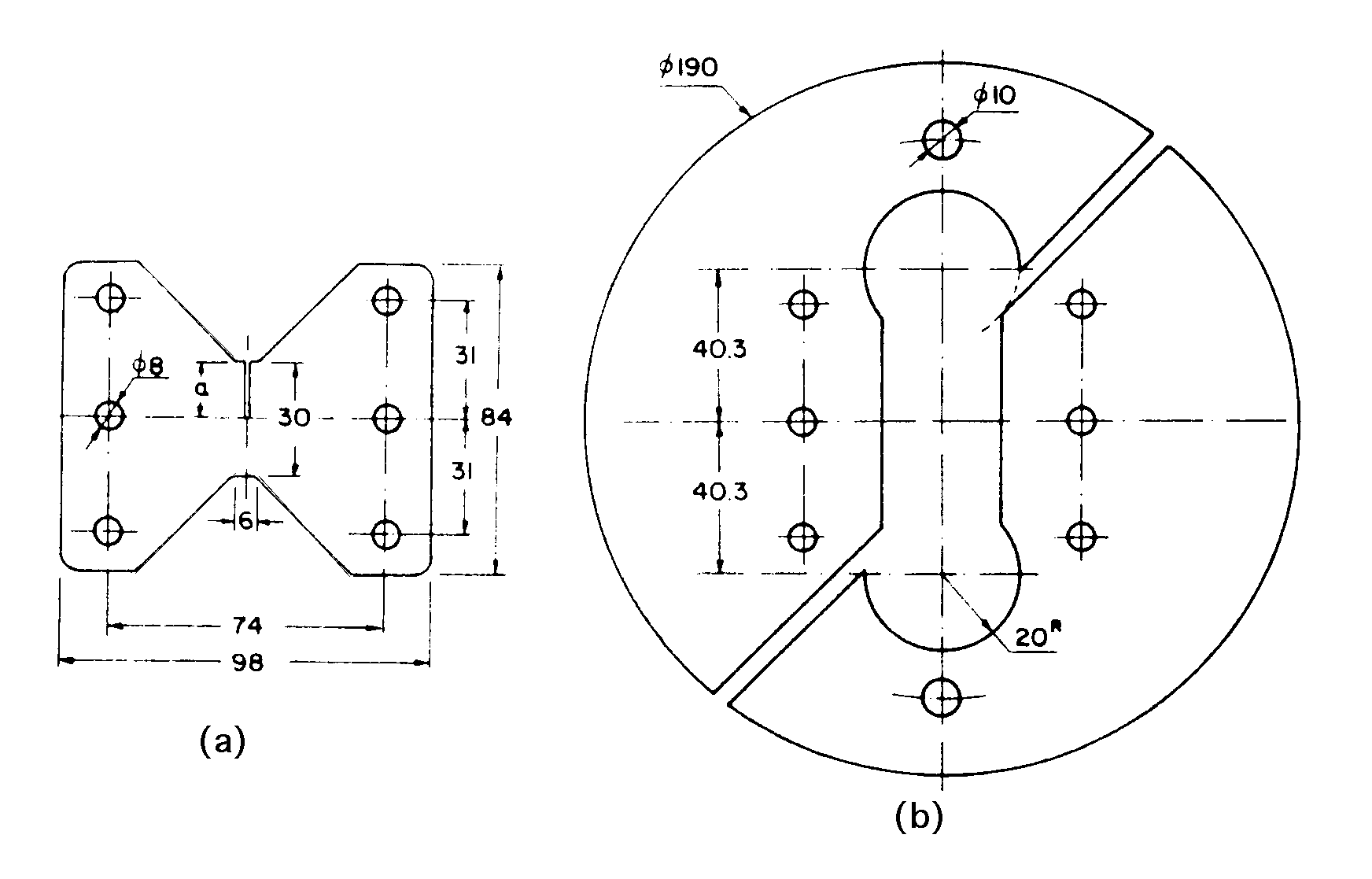
The test piece in the shape of a diabolo, represented in (a), is fixed to the loading system (b) by six pins equivalent to joints.
The dimensions of the pieces are expressed in mm.
Test tube:
thickness \(B\) variable |
\(\mathrm{6,36};\mathrm{6,39};\mathrm{6,44}\mathrm{mm}\) |
overall width |
\(98\mathrm{mm}\) |
distance between pin axes |
\(74\mathrm{mm}\) |
width of the central part |
\(6\mathrm{mm}\) |
overall height |
\(84\mathrm{mm}\) |
distance between pin centers |
\(31\mathrm{mm}\) |
center height \(W\) |
|
crack length \(a\) |
|
ligament \(b=W-a\) |
|
pin hole diameter |
\(8\mathrm{mm}\) |
Test tube holder:
thickness |
\(25\mathrm{mm}\) |
outside diameter |
\(190\mathrm{mm}\) |
distance between the center of the room and the centers of the circular recesses |
\(\mathrm{40,3}\mathrm{mm}\) |
radius of the recesses |
\(20\mathrm{mm}\) |
diameter of the 2 holes where the loads are applied |
\(10\mathrm{mm}\) |
1.2. Material properties#
Test tube:
The material is elastoplastic, of the Von Mises type, with isotropic work hardening, defined by a uniaxial tension curve.
Young’s module: \(E=\mathrm{74,2}\mathrm{GPa}\)
Poisson’s ratio: \(\nu =\mathrm{0,32}\)
\(E\) tangent (\(\mathrm{GPa}\)) |
\(\sigma \) uniaxial) (\(\mathrm{MPa}\)) |
\({\varepsilon }_{T}\) uniaxial) (\(\text{\%}\)) |
72.74 |
334.6 |
0.46 |
50.69 |
410.7 |
0.61 |
15.00 |
431.6 |
0.75 |
4.75 |
443.5 |
1.00 |
1.82 |
480.0 |
3.00 |
0.80 |
500.1 |
5.50 |
0.0017 |
505.2 |
300.0 |
Test tube holder:
The material is isotropic linear elastic.
Young’s module: \(E=206\mathrm{GPa}\)
Poisson’s ratio: \(\nu =\mathrm{0,3}\)
1.3. Boundary conditions and loading#
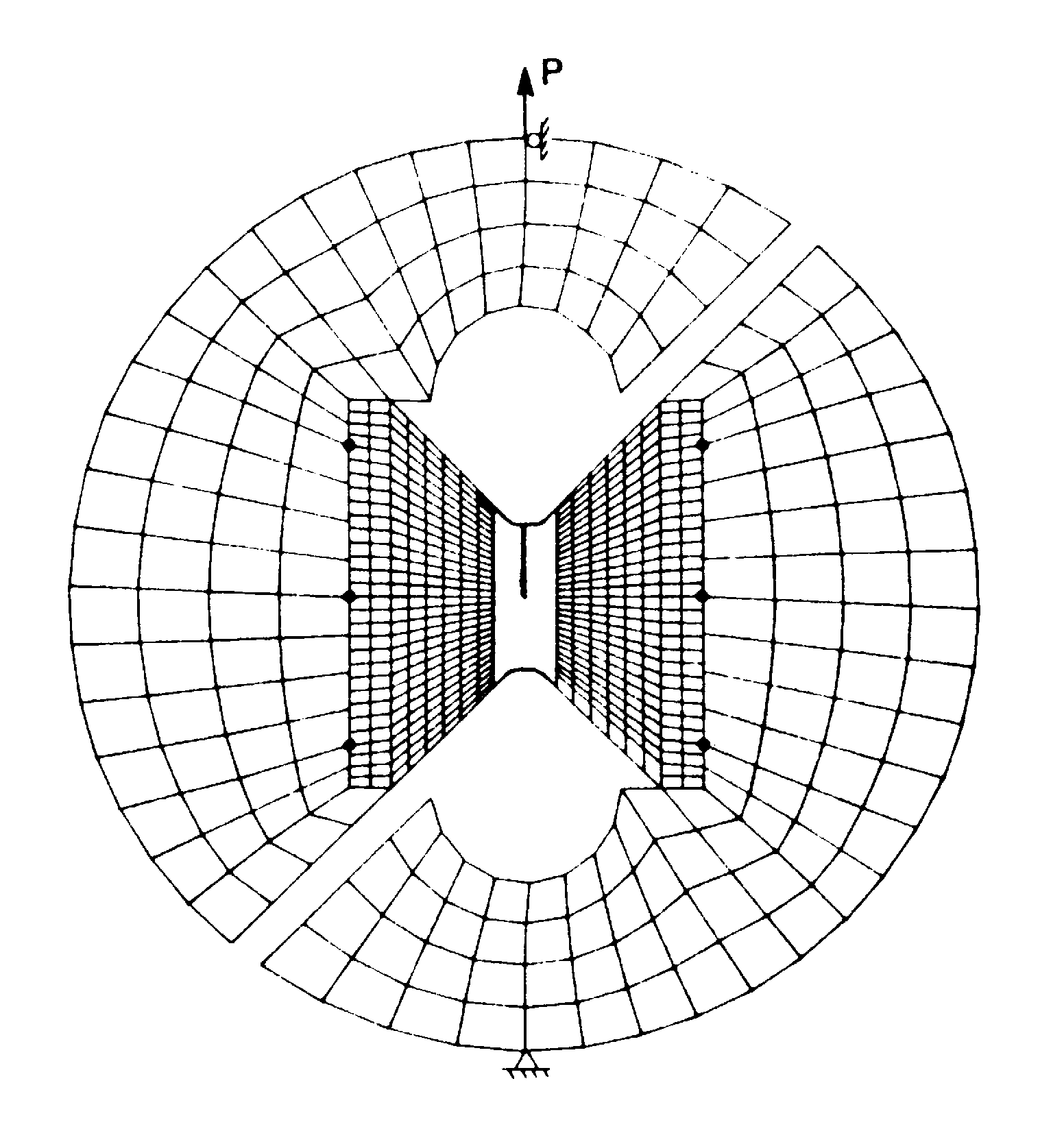
The specimen holder has a fixed point \(\mathrm{UX}=\mathrm{UY}=0\) at the lower attachment hole and is subject to a vertical point loading applied to the variable upper attachment hole \(\mathrm{UX}=0\), \(\mathrm{FY}=P\).
For crack length \(a/W=\mathrm{0,5}\):
\(P\) varies from:
\(0N\) to \(11772N\) in 12 steps from \(981N\)
\(11772N\) to \(19620N\) in 16 steps from \(\mathrm{490,5}N\)
\(19620N\) to \(23544N\) in 20 steps from \(\mathrm{196,2}N\)
\(23544N\) to \(25114N\) in 16 steps from \(\mathrm{98,1}N\)