1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#

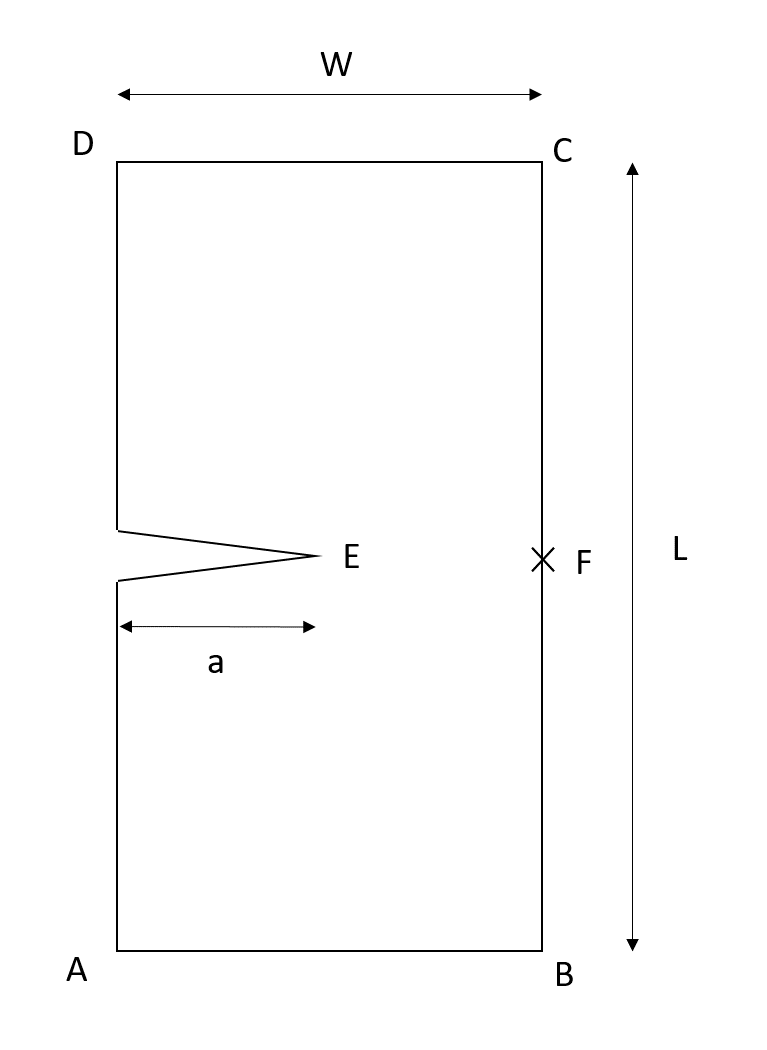
Length |
\(L=400\mathit{mm}\) |
Width |
\(W=100\mathit{mm}\) |
Crack depth |
\(a=50\mathit{mm}\) |
1.2. Material properties#
The material obeys a « non-linear » law of elastic behavior (Hencky’s law) from von Mises with linear isotropic work hardening (EMAS_VMIS_LINE).
The properties of the material are as follows:
Young’s module |
\(E=\mathrm{2,1}\times {10}^{5}\mathit{MPa}\) |
Poisson’s Ratio |
\(\mathrm{\nu }=0.3\) |
Linear elastic limit |
\({\mathrm{\sigma }}_{y}=150\mathit{MPa}\) |
Traction curve slope |
\(\text{D\_SIGM\_EPSI}=\mathrm{5,25}\times {10}^{4}\mathit{MPa}\) |
Expansion coefficient |
\(\mathrm{\alpha }={1.10}^{-5}\) |
Reference temperature |
\(\text{VALE\_REF}=20°C\) (AFFE_MATERIAU keyword) |
1.3. Boundary conditions and loading#
For models A and C, the model is limited to half of the structure, the horizontal plane of the crack being a plane of symmetry. For B and D models, the entire structure is represented.
Boundary conditions
A and C models:
Horizontal displacement \(\mathrm{UX}=0\) at point \(F\)
Vertical displacement \(\mathrm{UY}=0\) in ligament \(\mathit{EF}\) (symmetry condition)
B and D modeling:
Horizontal displacement \(\mathrm{UX}=0\) on segment \(\mathit{AB}\)
Vertical displacement \(\mathit{UY}=0\) on segment \(\mathit{AB}\)
Loading mechanical
A and C models:
Normal surface force applied to segment \(\mathit{CD}\)
B and D modeling:
Horizontal displacement imposed on segment \(\mathit{CD}\): \(\mathit{UY}=\mathrm{\delta }\)
Vertical displacement imposed on segment \(\mathrm{CD}\): \(\mathit{UX}=\mathrm{\delta }\)
Thermal load
A to C modeling:
No thermal loading.
D modeling:
Stationary temperature dependent on the \(x\) axis and increasing linearly between 0°C in \(x={x}_{A}=0\) and 200°C in \(x={x}_{B}=w\). The reference temperature is fixed at 100° C.