1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
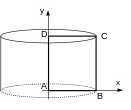
Figure 1.1-a : Problem geometry.
It is a cylinder with radius \(1\mathrm{mm}\) and height \(1\mathrm{mm}\).
The square in bold corresponds to axisymmetric modeling.
1.2. Material properties#
The material properties are dependent on the type of modeling and functions of the temperature in \(°C\) and on the irradiation in \(\mathrm{dpa}\) (displacement by atom).
The material parameters used in this test case should not be used for studies. They do not correspond to real characteristics.
For all models
Young’s module: \(E=210000.0–30.0T\) in \(\mathrm{MPa}\)
Poisson’s ratio: \(\nu =0.30+5.0E-05T\).
Coefficient of thermal expansion: \(\alpha =\left(15.0+0.002T\right)1.0E-06\)
For modeling a
Plastic part
\(\kappa =1.0\)
Elastic limit at 0.2% in \(\mathrm{MPa}\): \({R}_{02}={R}_{02}^{0}\mathrm{.}{C}_{w}\text{\_}{R}_{e}\mathrm{.}{I}_{r}\text{\_}{R}_{e}\)
with
\({R}_{02}^{0}=270.0-0.65T+0.001{T}^{2}\)
\({C}_{w}\text{\_}{R}_{e}=3.0\)
\({I}_{r}\text{\_}{R}_{e}=\left(2.0–{e}^{\frac{-\mathit{IRRA}}{3}}\right)\)
Ultimate compulsion in \(\mathrm{MPa}\): \({R}_{m}={R}_{02}(T,\mathrm{IRRA})+({R}_{m}^{0}–{R}_{02}^{0})\mathrm{.}{C}_{w}\text{\_}{R}_{m}\mathrm{.}{I}_{r}\text{\_}{R}_{m}\)
with
\({R}_{m}^{0}=600.0-1.5T+0.010{T}^{2}\)
\({C}_{w}\text{\_}{R}_{m}=0.50\)
\({I}_{r}\text{\_}{R}_{m}=0.25-0.10\left(1.0-{e}^{\frac{-\mathit{IRRA}}{10.0}}\right)+{e}^{\frac{-\mathit{IRRA}}{3.0}}\)
Distributed elongation: \({ϵ}_{u}=\mathrm{ln}(1.0+{ϵ}_{u}^{0}.{C}_{w}\text{\_}{ϵ}_{u}.{I}_{r}\text{\_}{ϵ}_{u}\ast 1.0E-02)\)
with
\({ϵ}_{u}^{0}=50.0-0.15T+0.0007{T}^{2}\)
\({C}_{w}\text{\_}{ϵ}_{u}=0.25\)
\({I}_{r}\text{\_}{ϵ}_{u}={e}^{\frac{-\mathit{IRRA}}{2}}\)
Irradiation part |
Swelling part |
\({A}_{\mathrm{i0}}=0.0{\mathrm{MPa}}^{-1}\mathrm{.}{\mathrm{dpa}}^{-1}\) \({\eta }_{\mathit{is}}=1.0E+50\mathit{MPa.dpa}\) |
\(\alpha =0.0\) \({\phi }_{\mathrm{0 }}=0.0\mathrm{dpa}\) |
For modeling b
Plastic part
\({R}_{02}=5.0E+09\mathit{Mpa}\) \({R}_{m}=5.0E+09\mathit{Mpa}\) \({\varepsilon }_{u}=0.0\)
Irradiation part |
Swelling part |
\({A}_{\mathit{i0}}=2.0E-06{\mathit{MPa}}^{-1}.{\mathit{dpa}}^{-1}\) \({\eta }_{\mathrm{is}}=1000.0\mathrm{MPa.dpa}\) |
\(\alpha =0.0\) \({\phi }_{0}=0.0\mathrm{dpa}\) |
For c modeling
Plastic part
\({R}_{02}=5.0E+09\mathit{Mpa}\) \({R}_{m}=5.0E+09\mathit{Mpa}\) \({\varepsilon }_{u}=0.0\)
Irradiation part |
Swelling part |
\({A}_{\mathrm{i0}}=0.0{\mathrm{MPa}}^{-1}\mathrm{.}{\mathrm{dpa}}^{-1}\) \({\eta }_{\mathit{is}}=1.0E+06\mathit{MPa.dpa}\) |
\(\alpha =1.0\) \({\phi }_{0}=1.0\mathrm{dpa}\) |
1.3. Boundary conditions and loads#
Modeling a
For edges \(\mathrm{AB}\) and \(\mathrm{DC}\), \(\mathrm{DY}=0\)
For edge \(\mathrm{AD}\), \(\mathrm{DX}=0\)
In addition, a linear temperature ramp with a maximum of \(400°C\) is applied.
Modeling b
For edge \(\mathrm{AB}\), \(\mathrm{DY}=0\)
For edge \(\mathrm{AD}\), \(\mathrm{DX}=0\)
For edge \(\mathrm{DC}\), apply a linear ramp of linear forces with a maximum value of \(\mathrm{FY}=\mathrm{200 }N/\mathrm{mm}\)
In addition, a linear irradiation ramp with a maximum of \(10\mathrm{dpa}\) and a temperature ramp with a maximum of \(400°C\) are applied.
C modeling
For the \(\mathrm{AB}\) \(\mathrm{DY}=0\) edge
For the \(\mathrm{AD}\) \(\mathrm{DX}=0\) edge