3. Modeling A#
3.1. Characteristics of modeling#
C- PLAN, TRI6 and QUAD8 meshes
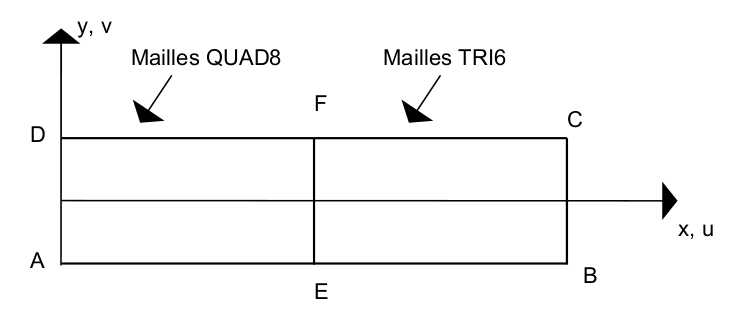
Point \(E\) = middle of \(\mathit{AB}\) point \(F\) = middle of \(\mathit{CD}\)
Node name:
Point \(A\mathrm{=}\mathit{N1}\) |
Point \(D\mathrm{=}\mathit{N403}\) |
Point \(B\mathrm{=}\mathit{N455}\) |
Point \(E\mathrm{=}\mathit{N201}\) |
Point \(C\mathrm{=}\mathit{N756}\) |
Point \(F\mathrm{=}\mathit{N352}\) |
3.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
Number of knots: 905
Number of meshes and types: 100 QUAD8, 200 TRIA6, 200, 208 SEG3
3.3. Tested values#
Location |
Value type |
Reference |
% difference |
Points \(B\), \(C\) |
|
0.129 |
0.4 |
Point \(A\) |
|
2,04E+8 |
2.3 |
Point \(E\) |
|
1.02E+8 |
0.5 |
3.4. notes#
The difference with the analytical solution, such as a beam or slender plate, is due to the modeling used: the dimensions of the structure, which is very slender, do not in fact make it possible to respect the plane stress conditions.