1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
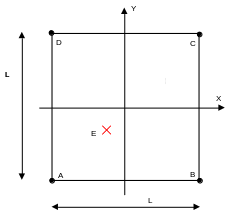
Geometry of plate \((m)\):
\(L=1\)
\(e=0.001\) thickness
Coordinates of points \((m)\):
\(O(0.0,0.0)\)
\(E(-0.1,-0.1)\)
Mesh group:
\(\mathrm{CONT}\text{\_}\mathrm{NO}\): \(\mathrm{AB},\mathrm{BC},\mathrm{CD},\mathrm{DA}\) sides
\(\mathrm{COND2}\text{\_}\mathrm{NO}\): Face \(\mathrm{ABCD}\) except point \(E\)
1.2. Elastic properties of the material#
\(E=7.1E10\mathrm{Pa}\) Young’s module
\(\nu =0.3\) Poisson’s ratio
\(\rho =7820.0{\mathrm{kg.m}}^{-3}\) Density
\(\mathrm{AMOR}\text{\_}\mathrm{ALPHA}=0.5{\mathrm{N.s.m}}^{-1}\)
\(\mathrm{AMOR}\text{\_}\mathrm{BETA}=0.1{\mathrm{N.kg}}^{-1}\)
The coefficients \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) make it possible to build a viscous damping matrix that is proportional to stiffness and mass: \([C]=\alpha [K]+\beta [M]\).
1.3. Boundary conditions and loads#
Imposed travel:
\(\mathrm{CONT}\text{\_}\mathrm{NO}\): zero movements and rotations
\(\mathrm{COND2}\text{\_}\mathrm{NO}\): zero movements and rotations
Excitation force \((N)\):
Point \(E\): \(\mathrm{Fz}=1\)