1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
The pipe is a hollow cylinder with a circular cross section, filled with fluid.
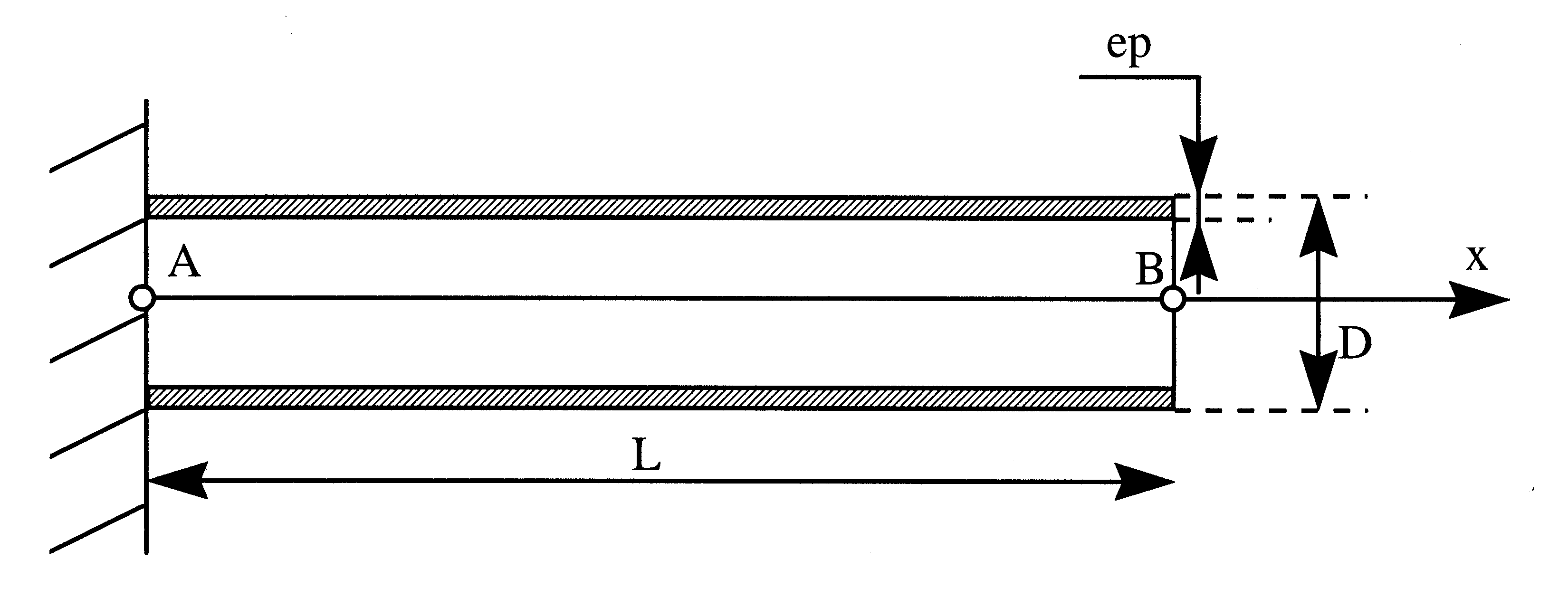
Characteristics of the pipe:
length: |
\(L=\mathrm{1,0}m\) |
outside diameter: |
\(D=\mathrm{0,1}m\) |
thickness: |
\(\mathrm{ep}=\mathrm{0,01}m\) |
For modeling C, the section is modified, which becomes variable: the diameter varies from 0.1 to 0.11 m while the thickness varies from 0.011 to 0.01 m.
1.2. Material properties#
The physical characteristics of the material constituting the tube are as follows:
Young’s modulus: \(E=\mathrm{1,0}·{10}^{10}\mathrm{Pa}\)
Poisson’s ratio: \(\nu =\mathrm{0,3}\)
density: \({\rho }_{s}=\mathrm{1,0}·{10}^{4}\mathrm{kg}/{m}^{3}\)
Longitudinal wave speed: \({c}_{s}=\sqrt{\frac{E}{{\rho }_{s}}}=\mathrm{1,0}·{10}^{3}m/s\)
The physical characteristics of the fluid material in the tube are as follows:
density: \({\rho }_{f}=\mathrm{1,0}·{10}^{3}\mathrm{kg}/{m}^{3}\)
speed of sound: \({c}_{f}=\mathrm{1,0}·{10}^{3}m/s\)
1.3. Boundary conditions and loading#
* Movement only along the :math:`x` axis.
* Embedding the pipe at the :math:`A` end.
* Free tubing at the :math:`B` end.
* For the fluid reservoir condition at the :math:`A` end.