1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
We consider a cylinder with radius \(1\mathit{cm}\) and height \(1\mathit{cm}\) (i.e. a mesh corresponding to a square domain of \(1\mathit{cm}\mathrm{\times }\mathrm{1cm}\), the modeling being axisymmetric).
1.2. Material properties#
Here, parameters corresponding to argillite are selected in order to obtain a realistic thermal pressurization coefficient.
Liquid water |
Density \(({\mathrm{kg.m}}^{-3})\) Specific heat at constant pressure \(({\mathrm{J.K}}^{-1})\) Dynamic viscosity of liquid water \((\mathrm{Pa.s})\) Coefficient of thermal expansion of liquid \(({K}^{-1})\) (if constant, see next section) Compressibility \(({\mathit{Pa}}^{\mathrm{-}1})\) |
\(4180\) \(0.001\) \(1.{10}^{-4}\) \({K}_{e}=5.{10}^{-10}\) |
Solid |
Drained Young’s Module \(E(\mathrm{Pa})\) Poisson’s ratio Coefficient of thermal expansion of solid \(({K}^{-1})\) |
\(0.375\) \({10}^{-5}\) |
Reference state |
Porosity Temperature \((K)\) Liquid pressure \((\mathrm{Pa})\) |
\(273\) \(0\) |
Homogenized coefficients |
Homogenized density \(({\mathrm{kg.m}}^{-3})\) Biot coefficient Intrinsic permeability \(({m}^{2})\) Thermal conductivity |
\(2410\) \(0.6\) \({K}_{\text{int}}={10}^{-21}\) \({\lambda }_{T}=1.61\) |
1.3. Boundary conditions and loads#
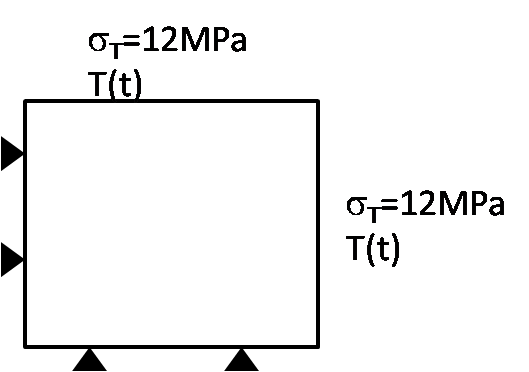
We impose:
On the bottom and left edges: zero displacements, zero hydraulic flow, zero heat flow. These are symmetry conditions.
On the top and right edges: Total stress imposed on \(12\mathit{MPa}\), zero hydraulic flow, temperature imposed as a function of time \(T(t)\) following a linear ramp such as:
\(T(t)={T}_{0}+\frac{\Delta T}{{t}_{s}}\) where \({t}_{s}\) corresponds to the simulation time (here \({t}_{\mathit{sim}}\mathrm{=}\mathrm{1h}\)) and \(\Delta T\) the temperature variation imposed during this time (here \(\Delta T\mathrm{=}40°C\)).
1.4. Initial conditions#
\(P(x)\mathrm{=}\mathrm{4MPa}\) and \(T(x)\mathrm{=}{T}_{0}\mathrm{=}20°C\) everywhere.