1. General characteristics#
1.1. Geometry#
The three-point flexure beam studied is 5m long. Its section is 0.2x0.5m. Its geometry as well as the positioning of the steels that constitute it are defined on the.
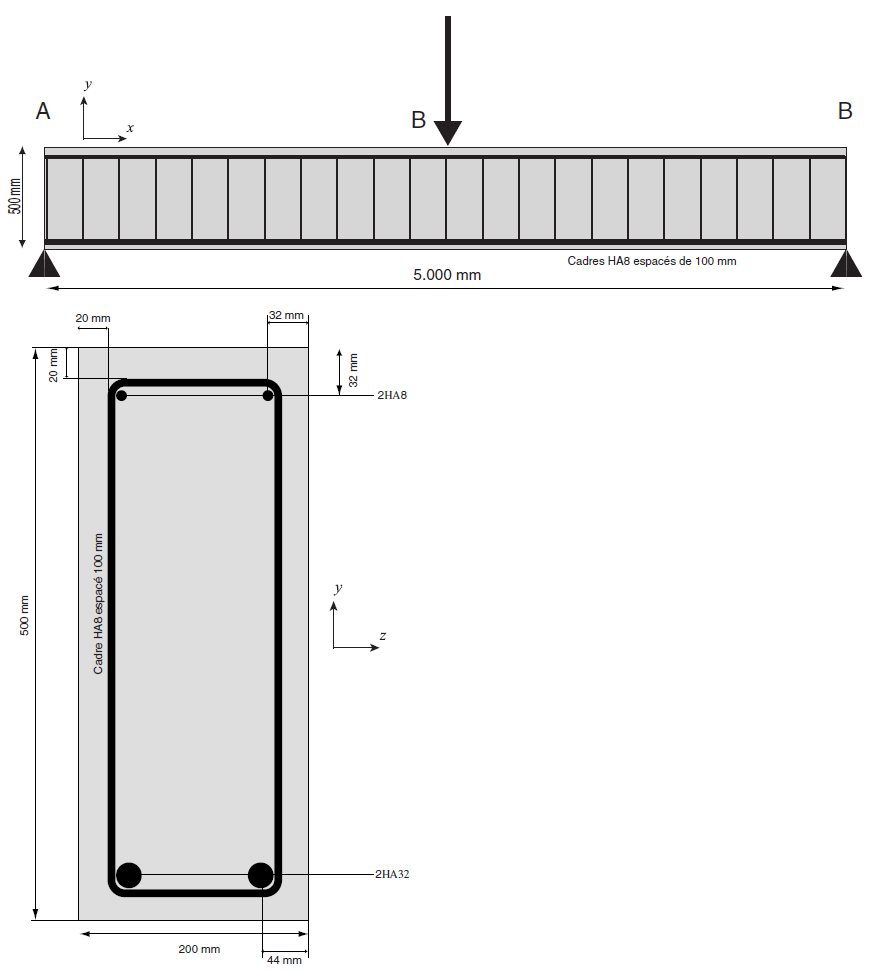
Figure 1.1-a: Beam plane.
1.2. Material properties#
Concrete: resistance class” C30/37 “or” C35/45 “
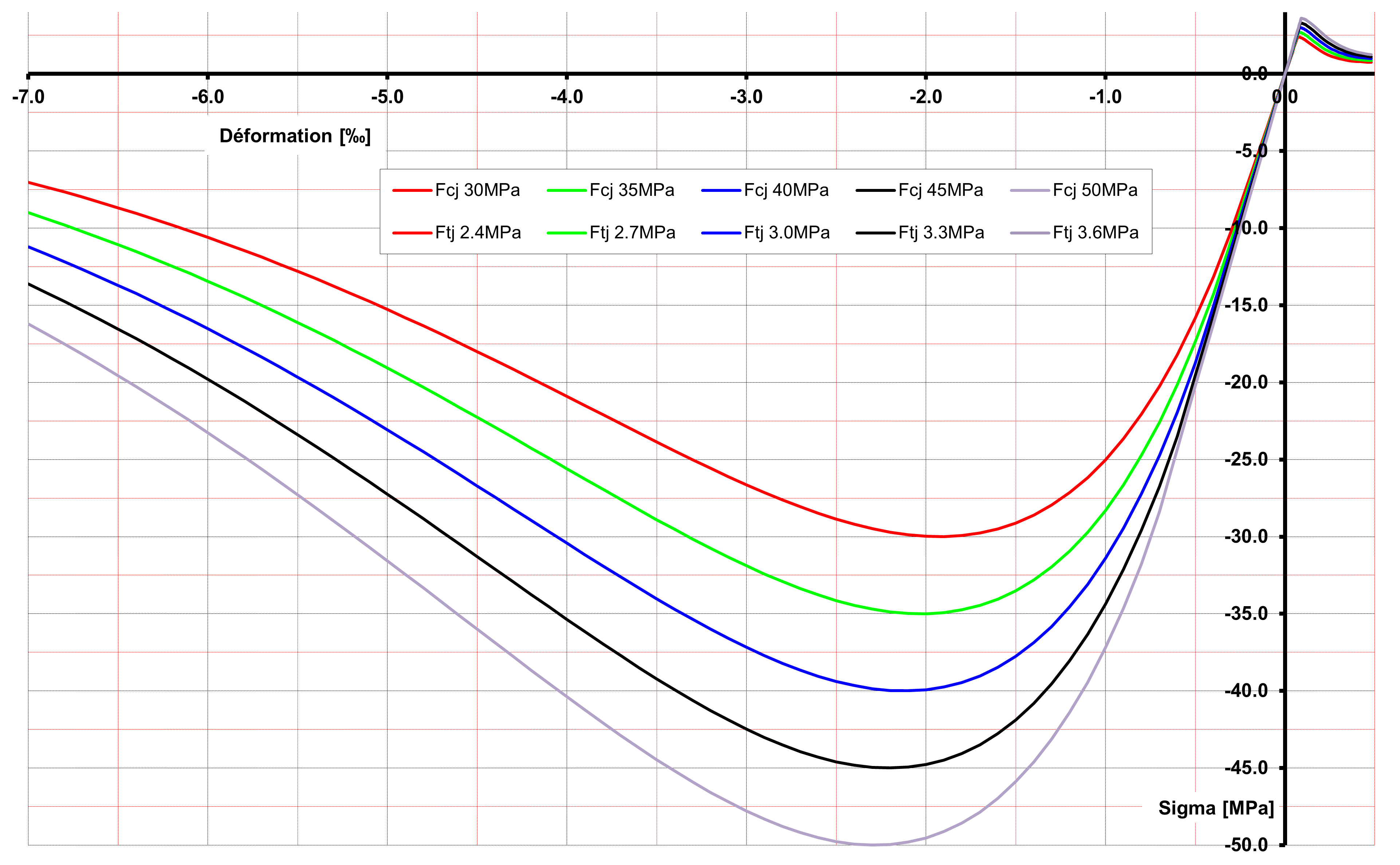
Figure 1.2-a : Examples of answers with the Mazars 1D law.
Steel:
FE400: \({f}_{\mathit{yk}}=400\mathit{MPa}\) Tangent module (plastic slope) \({E}_{T}=1200\mathit{MPa}\) |
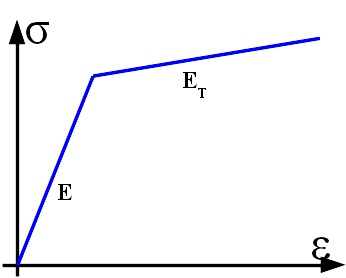
Figure 1.2-b : C C curve stress — deformation of steel. |
1.3. Boundary conditions and loads#
Simple press in \(B\): \(\mathit{DY}=0\).
Double press in \(A\): \(\mathit{DX}=\mathit{DY}=\mathit{DZ}=0\) as well as \(\mathit{DRX}=\mathit{DRY}=0\).
Quasi-static loading: monotonic downward displacement \(\mathit{DY}\) applied halfway through \(C\) (3-point flexure test), according to a linear function of time:
\(t\) |
|
\(\mathrm{0,0}\) |
|
\(\mathrm{3,0}\) |
|
\(\mathrm{5,0}\) |
|