1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
We consider a beam of length \(2m\) oriented along \(X\).

1.2. Section characteristics#
1.2.1. Geometry and fibers#
The section under consideration is a square with a side of \(10\mathit{cm}\). It is composed of 16 fibers, which are themselves square in shape.
1.2.2. Materials#
The section has two different materials that are described in the following table.
Material |
Concrete |
Steel |
Young Module |
\(3\mathrm{\times }{10}^{10}\mathit{Pa}\) |
|
Fish Coefficient |
\(0.2\) |
|
Density |
\(2500\mathit{kg}/{m}^{3}\) |
|
Symbol on the figure |
\(B\) |
|
The materials are affected on the fibers as illustrated in the following figure:
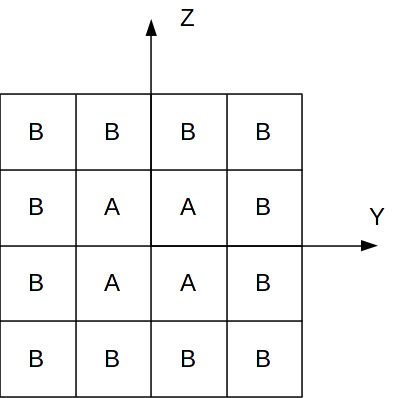
This structure has the advantage of keeping the centers of stiffness, gravity, and torsional combined at the origin of the local coordinate system of the section and of being symmetric with respect to its center and with respect to the axes \(Y\) and \(Z\).
1.3. Loads#
1.3.1. Boundary conditions#
Static calculation:
Node \(A\) is embedded and node \(B\) is left free.
Modal calculation:
The movements of node \(A\) are blocked as well as the rotation around the axis of the beam.
The movements in \(Y\) and \(Z\) of the node \(B\) are blocked as well as the rotation around the axis of the beam.
1.3.2. Applied forces#
Static calculation:
A constant distributed force of \(\mathrm{-}1.0E+04N\mathrm{/}m\) according to \(Z\) is applied to the beam.
Modal calculation:
None.