1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
A cable of length \(2{l}_{0}\) at rest, in the direction \(x\), is subjected to its own weight (gravity in direction \(-Z\)). It is embedded at the \(O\) and \(B\) ends, which are themselves distant from \(\mathrm{2L}\).
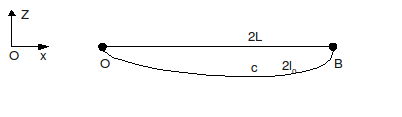
Initially, \(2{l}_{0}=2L=\mathrm{325m}\)
The cable cross-sectional area is: \(2.2783E-04{m}^{2}\)
1.2. Material properties#
\(E=5.70E+10\mathrm{Pa}\)
\(\nu =0.3\) (B modeling only)
\(\mathrm{ALPHA}:2.3E-5{K}^{-1}\)
\(\mathrm{RHO}:2.844230E+03\mathrm{kg}/{m}^{3}\)
1.3. Boundary conditions and loads#
Embedding in \(O\) and \(B\)
Gravity: \((9.81\mathrm{,0}.0\mathrm{,0}.0,-1.0)\)
The temperature in the cable varies over time, the reference temperature is \(0.°C\).
Instant: 0. Temperature \(T=0.°C\)
Instant: 1.Temperature \(T=39.26°C\)
We therefore treat:
at instant 0, a cable subject to its own weight alone
at instant 1, a heavy cable subjected to thermal expansion.