1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
Bar length |
: \(1m\) |
Bar section |
: \(5{\mathrm{cm}}^{2}\) |
1.2. Material properties#
1.2.1. Isotropic hardening and linear kinematics#
Young’s module: |
\(E=2.{10}^{11}\mathrm{Pa}\) |
Work hardening slope: |
\({E}_{t}={2.10}^{9}\mathrm{Pa}\) |
Elastic limit: |
\(\sigma ={2.10}^{8}\mathrm{Pa}\) |
Poisson’s ratio: |
\(\nu =\mathrm{0,3}\) |
Coefficient of thermal expansion: |
\(\alpha ={1.10}^{-5}{K}^{-1}\) |
1.2.2. Pinto-Menegotto model#
1.3. Boundary conditions and loading#
Boundary conditions:
The bar is recessed. Travel is therefore blocked in all three directions.
In \(\mathrm{N1}\) and \(\mathrm{N2}\): \(\mathrm{DX}=\mathrm{DY}=\mathrm{DZ}=0\)
Charging:
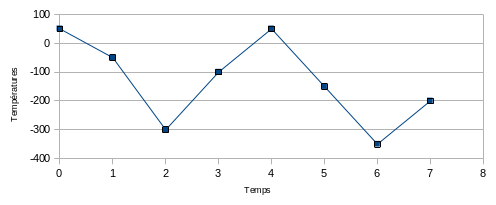
The loading path is described by the evolution of the temperature, which is uniform across the bar:
\(t\) |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
\(T(°C)\) |
50 |
—50 |
—50 |
—300 |
—300 |
—100 |
—150 |
—350 |
—200 |
The reference temperature is \(0°C\).