4. B modeling#
4.1. Characteristics of modeling#
4.2. Characteristics of the mesh#
Number of knots: 224
Number of meshes and type: 384 TRIA3
4.3. Tested values#
Identification |
Reference [bib1] |
Reference [bib2] |
Aster |
% differences |
||
Move \(w\) to point \(F\) |
|
|
|
|||
Move \(w\) to point \(C\) |
|
|
|
|||
Move \(w\) to point \(D\) |
|
|
|
|||
Constraint \(\mathit{SIXX}\) at point \(F\) |
|
|
|
|||
Constraint \(\mathit{SIYY}\) at point \(F\) |
|
|
|
4.4. notes#
Values for the CISA_L and CISA_T coefficients are not available. As the structure is thin (\(h/R=0.045\)), it is assumed that the effects of transverse shear are negligible, so we imposed CISA_L = CISA_T = \({10}^{10}\).
The normal displacement w is expressed in the local cylindrical coordinate system \((R,\theta ,z)\), it is the displacement normal to the shell element.
4.5. Value of the normal displacement along CD#
The results obtained with a TRIA3 mesh are very similar to those obtained with the QUAD4 mesh.
4.6. Stress value along CD#
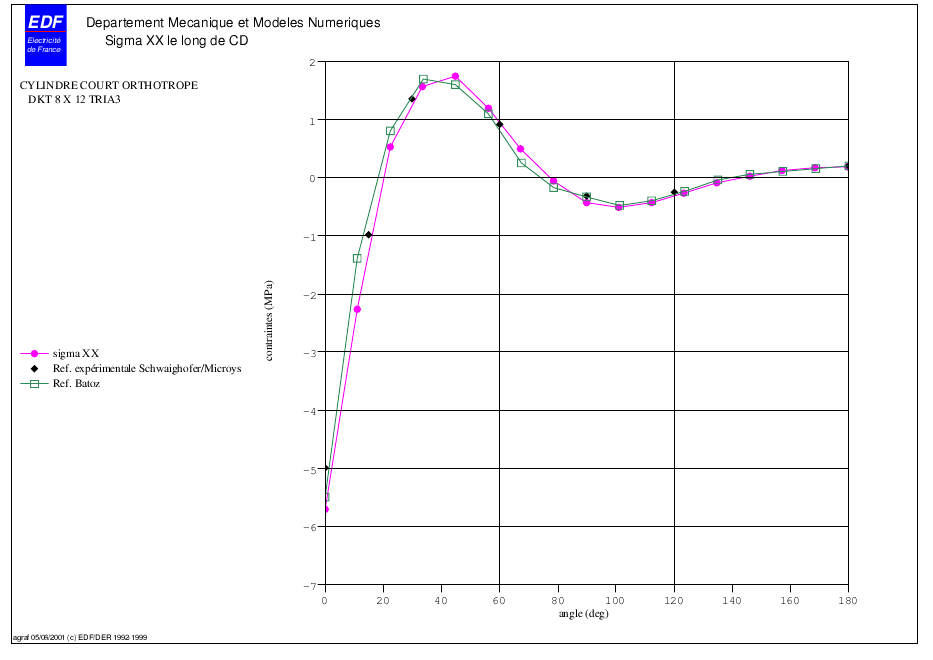
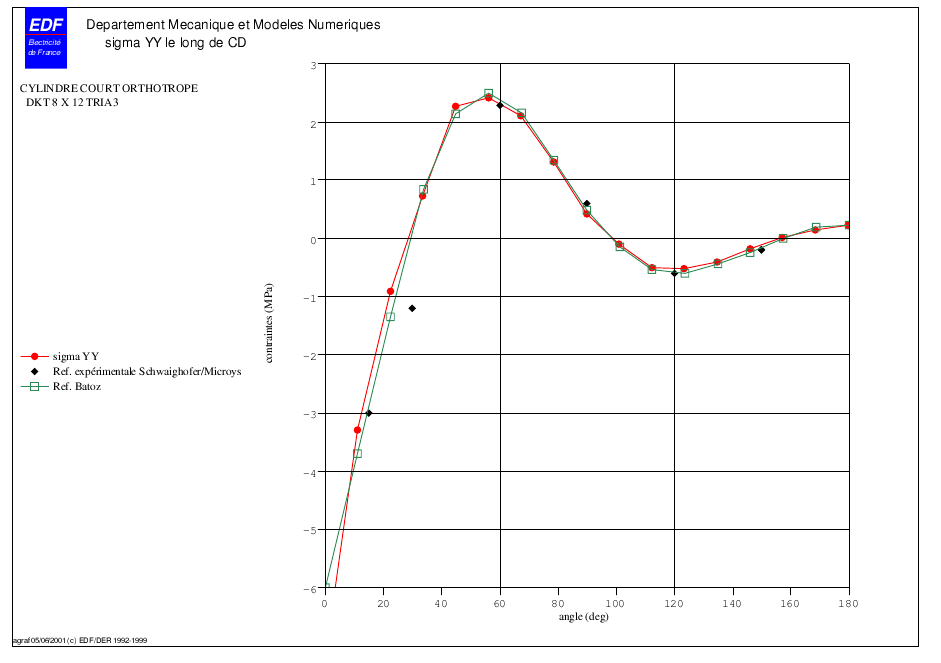
The stress profiles obtained by B modeling with TRIA3 are generally close to Batoz solutions.