1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
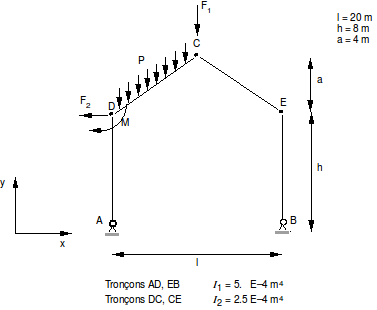
Gantry geometry \((m)\):
\(l=20\)
\(h=8\)
\(a=4\)
Quadratic moments of beams \(({m}^{4})\):
Sections \(\mathrm{AD}\), \(\mathrm{EB}\): \({I}_{1}=5.0{E}^{-4}\)
Sections \(\mathrm{DC}\), \(\mathrm{CE}\): \({I}_{1}=2.5{E}^{-4}\)
The gantry consists of beams with symmetrical sections, so that \(\mathrm{IY}=\mathrm{IZ.}\)
Only the flexural energy is taken into account, because the beams are very slender. This is why the other beam cross-section characteristics do not come into play.
1.2. Material properties#
Isotropic linear elastic material: \(E=2.1\mathrm{E11}\mathrm{Pa}\)
1.3. Boundary conditions and loads#
Articulated \(A\) and \(B\) post legs.
Loading
Nodal strength in \(C\): |
\(Fy=–2000N=F1\) |
Nodal strength in \(D\): |
\(Fx=–10000N=F2\) |
Moment in \(D\): |
\(\mathrm{Mx}=–100000\mathrm{N.m}=M\) |
Force distributed over section \(\mathrm{DC}\): |
\(Pz=–3000N/m\) |