1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
The chimney is a vertical beam of length \(10m\), embedded at its base and articulated at two altitude points \(4m\) and \(8m\).
Beam cross section:
Area: \(A\mathrm{=}3.4390{10}^{\mathrm{-}3}{m}^{2}\)
Moments of inertia: \({I}_{y}\mathrm{=}\mathrm{1.3770.}{10}^{\mathrm{-}5}{m}^{4}\)
\({I}_{z}\mathrm{=}\mathrm{1.3770.}{10}^{\mathrm{-}5}{m}^{4}\)
\({J}_{x}\mathrm{=}2.7540{10}^{\mathrm{-}5}{m}^{4}\)
1.2. Material properties#
Beam |
Young’s module density Poisson’s ratio |
\(E\mathrm{=}1.658{10}^{11}\mathit{Pa}\) \(\rho \mathrm{=}1.3404106{10}^{4}\mathit{kg}\mathrm{/}{m}^{3}\) \(\nu \mathrm{=}\mathrm{0,3}\) |
1.3. Boundary conditions and loads#
Modeling A (3D)
Embedded point \(\mathit{N1}\): \(\mathit{DX}\mathrm{=}\mathit{DY}\mathrm{=}\mathit{DZ}\mathrm{=}\mathit{DRX}\mathrm{=}\mathit{DRY}\mathrm{=}\mathit{DRZ}\mathrm{=}0\)
Points \(\mathit{N5}\) and \(\mathit{N9}\) attached: \(\mathit{DX}\mathrm{=}\mathit{DY}\mathrm{=}0\)
Spectra of horizontal oscillators under acceleration applied to points \(\mathit{N1}\), \(\mathit{N5}\) and \(\mathit{N9}\) in the (\(x\)) and (\(x\) and \(y\)) directions.
Modeling B (2D plane \(\mathit{XZ}\))
Problem plan \(\mathit{XZ}\): \(\mathit{DY}\mathrm{=}\mathit{DRX}\mathrm{=}\mathit{DRZ}\mathrm{=}0\)
Embedded point \(\mathit{N1}\): \(\mathit{DX}\mathrm{=}\mathit{DZ}\mathrm{=}\mathit{DRY}\mathrm{=}0\)
Points \(\mathit{N5}\) and \(\mathit{N9}\) attached: \(\mathit{DX}\mathrm{=}0\)
Spectra of accelerating horizontal oscillators applied to points \(\mathit{N1}\), \(\mathit{N5}\) and \(\mathit{N9}\) in the (\(x\)) direction.
Spectra of identical values for the 3 amortizations \(\text{0,5\%}\), \(\text{1\%}\) and \(\text{1,5\%}\).
Frequency (\(\mathit{Hz}\)) |
Pseudo-acceleration (\({\mathit{m.s}}^{\mathrm{-}2}\)) in \(x\) |
Pseudo-acceleration (\({\mathit{m.s}}^{\mathrm{-}2}\)) in \(y\) |
1 10 30 100 10000 |
1.962 19.62 19.62 1.962 1.962 |
1.962 19.62 19.62 1.962 1.962 |
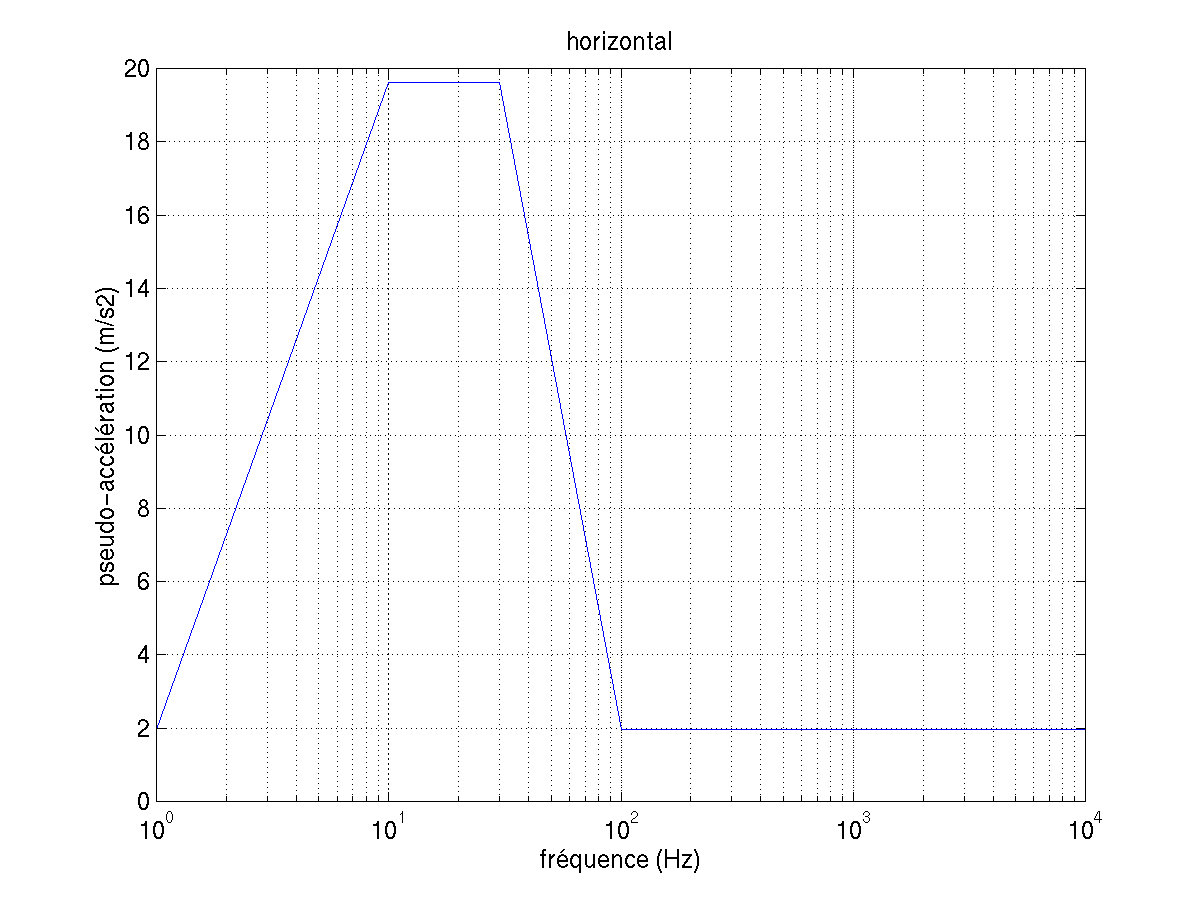
For the calculation, a damping reduced by 3% is used, with an interpolation (LOG LOG) in frequency and (LIN LOG) in damping.
Multi-support case with different excitations:
point \(\mathit{N1}\): excitement \(1\)
point \(\mathit{N5}\): excitement \(\mathrm{\times }1.5\)
point \(\mathit{N9}\): excitement \(\mathrm{\times }2\)
1.4. Initial conditions#
Not applicable for spectral analysis