1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
We consider a floor column resulting from the sdnx100 test case, whose main characteristics are described below:
The floor
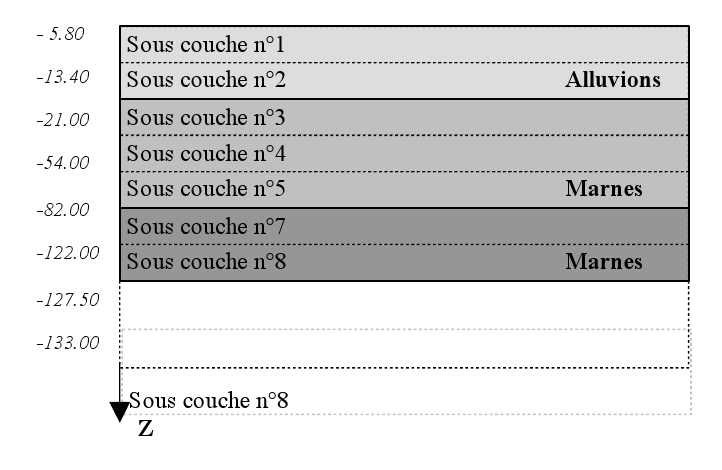
Laminate flooring configuration
1.2. Material properties#
1.2.1. Elastic properties of the material#
The mechanical characteristics of the soil model layers that were used are summarized in the table below:
Layer |
Sub-layer |
\(\mathrm{vs}(m/s)\) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1 |
1 |
184 |
2.67 108 |
2.67 108 |
2650 |
0.49 |
2.5 |
7.6 |
5.0 |
0 |
|
1 |
2 |
206 |
3.35 108 |
3.35 108 |
2650 |
0.49 |
2.5 |
7.6 |
5.0 |
0 |
|
2 |
3 |
340 |
9.21 108 |
9.21 108 |
2710 |
0.47 |
2.5 |
33.0 |
5.0 |
0 |
|
2 |
4 |
417 |
1.39 109 |
1.39 109 |
2.5 |
34.0 |
5.0 |
5.0 |
0 |
0 |
|
2 |
5 |
496 |
1.96 109 |
1.96 109 |
2.5 |
34.0 |
5.0 |
5.0 |
0 |
0 |
|
3 |
6 |
620 |
3.02 109 |
3.02 109 |
2710 |
2710 |
0.45 |
2.5 |
5.50 |
5.0 |
0 |
3 |
7 |
870 |
5.95 109 |
5.95 109 |
2710 |
2710 |
0.45 |
2.5 |
5.50 |
5.0 |
0 |
4 |
8 |
2500 |
4.23 1010 |
4.23 1010 |
2710 |
0.25 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
0 |
The values of SPT (\({N}_{1}\)) are provided equal to zero in order to test the computer operation of the macrocontrol only for modeling E with the Byrne model.
1.2.2. Shear modulus degradation and damping increase curves#
The three materials (alluvium and two types of marl) have curves of degradation of the elastic modulus G and of hysteretic damping given by the following curves:

|

|
1.3. Boundary conditions and mechanical loads#
1.3.1. Boundary condition#
The boundary conditions applied to the column during the dynamic calculation phase are as follows:
Bottom of the column: Assignment of an absorbent border element.
If 1D calculation — 1 component:
Right and left edges of the column: Periodicity condition. This means that the movements of the nodes on the left and right faces facing each other are made equal.
If 1D calculation — 3 components:
Side edges: Penalty rate encircling the column, so as to ensure a unique response in horizontal directions (stratified half-space hypothesis)
1.3.2. Loading#
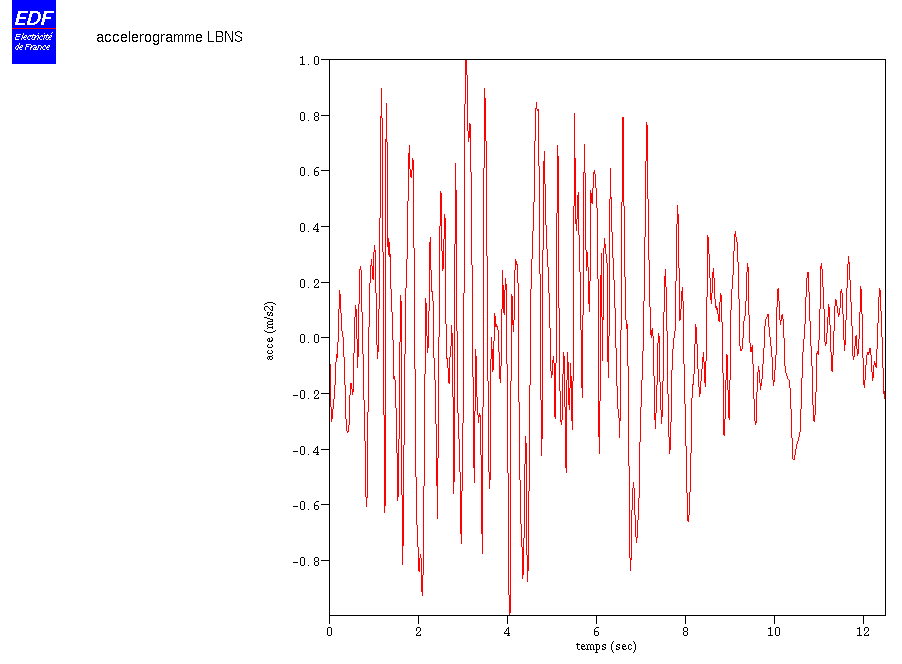
Transient acceleration in the ground given by functions LBNS. If free-field → outcropping rock deconvolution calculation, a coefficient of \(1.5\) is applied. If flush rock → free field convolution calculation, a coefficient of \(0.3\) is applied.