2. Modeling A#
2.1. Characteristics of the mesh#
The structure is modelled by a regular mesh composed of \(8\times 8\) TRIA6, respectively along the \(x,y\) axes. The interface is not meshed.
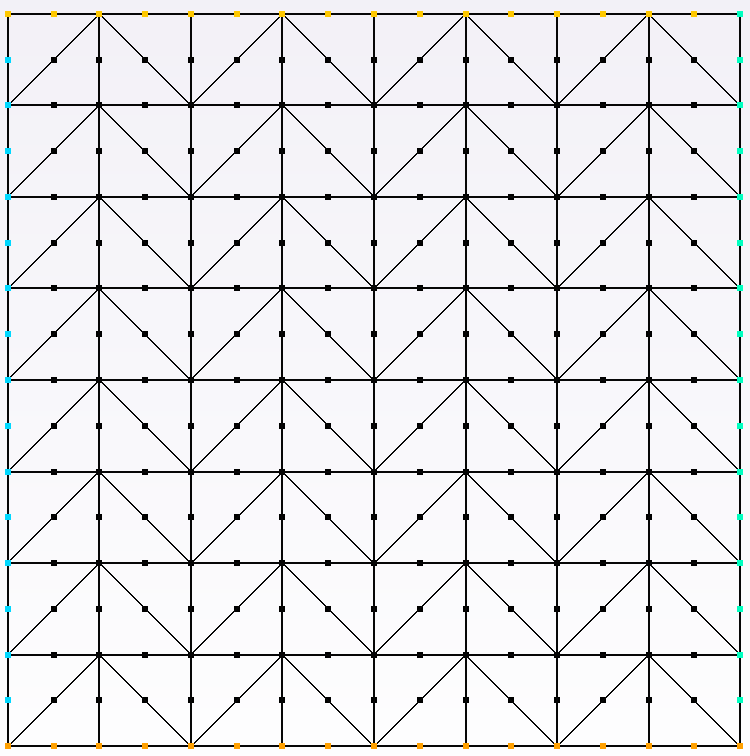
Figure 2.1-1 : Plate mesh (TRI6)
2.2. Tested sizes and results#
The bifurcation is located along an edge, on the segment of vertex nodes \((\mathrm{0,}0.5)\), \((\mathrm{0,}0.625)\) and middle node \((\mathrm{0,}0.5625)\). The fork takes place precisely at point \((\mathrm{0,}0.55)\) and the interface does not go through the middle node.
We then test the movement on the middle node positioned in \((\mathrm{0,}0.5625)\), to verify that it is positioned on the « right » side of the interface.
Identification |
Reference |
Tolerance |
DEPL_X |
||
NO_M: H1X |
1.0 |
1E -12% |
NO_M: DX |
1.0 |
1E -12% |
2.3. Additional results#
We find the « regularization » of the bifurcation in the vicinity of the coordinate point \((\mathrm{0,}0.55)\).
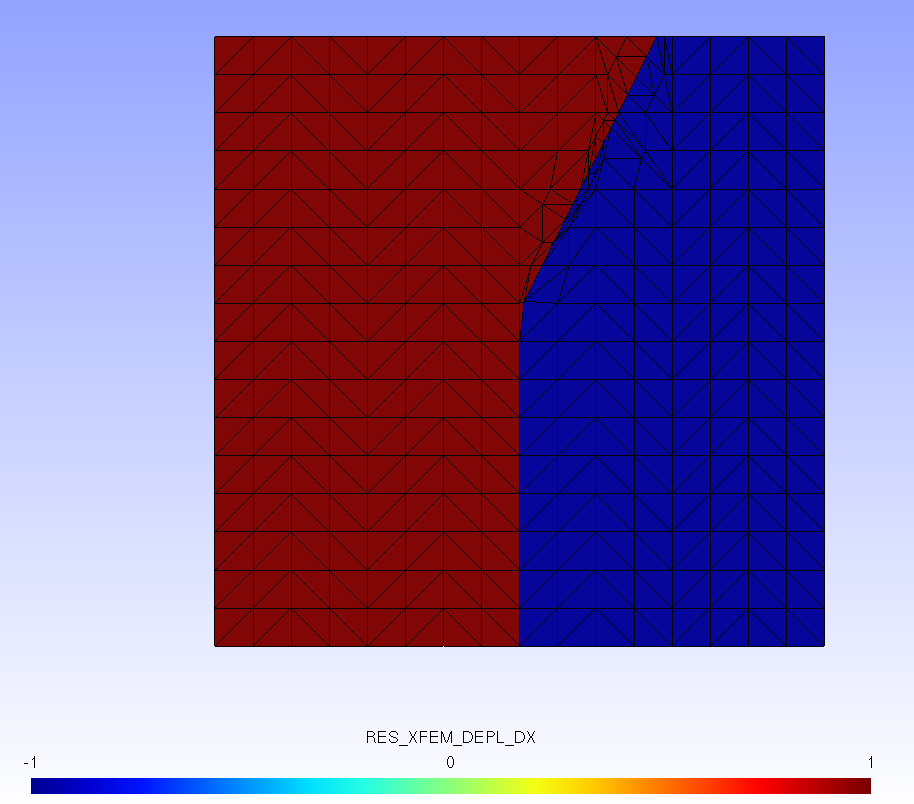
Figure 2.3-1 : Field of movement along X for the fork « before » the midpoint