3. Operands#
The POST_K_BETA operator can be used for axisymmetric or three-dimensional models.
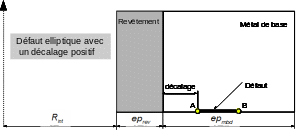
In the figures below we show a diagram of a tank slice with the presence of an elliptical defect (negative and positive offset) or a semi-elliptical defect.
Offset elliptical defect in the base metal
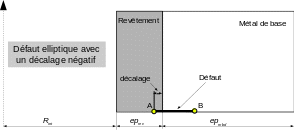
Offset elliptical defect in the coating
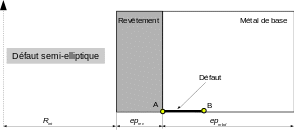
Semi-elliptical defect located under the coating
3.1. Operand MAILLAGE#
Mesh-type concept.
3.2. Operand MATER_REV#
Name of the material-type concept defining the material constituting the coating. Needed to recover:
Young’s modulus, for calculating influence coefficients (semi-elliptic defect),
Elastic limits, for the plastic correction of stress intensity factors.
3.3. Operand EPAIS_REV#
Coating thickness. Needed for:
The calculation of stress intensity factors in the case of the influence coefficients method (semi-elliptical defect)
The correction of stress intensity factors by edge factors and for plastic correction.
3.4. Operand MATER_MDB#
Name of the material-type concept that defines the material that makes up the base metal. Necessary to recover the Young’s modulus, for the calculation of the influence coefficients (semi-elliptical defect).
3.5. Operand EPAIS_MDB#
Thickness of the base metal, necessary for the correction of stress intensity factors by the method of coefficients of influence (semi-elliptical defect).
3.6. Keyword FISSURE#
Keyword factor for the geometric characterization of the defect. It can only be used once.
3.6.1. Operand FORM_FISS#
Defect shape: |
“ELLIPSE “for an elliptical defect, |
“SEMI_ELLIPSE “for a semi-elliptic defect, |
3.6.2. Operand DECALAGE#
This operand is only used in the case of a “ELLIPSE” shape defect. From the coating/base metal interface, it makes it possible to offset the crack in the:
Coating: DECALAGE negative,
Base metal: DECALAGE positive or zero.
3.6.3. Operand PROFONDEUR#
Radial dimension of the defect.
3.6.4. Operand LONGUEUR#
Second dimension of the defect (axial or orthoradial depending on the orientation of the defect).
3.6.5. Operand ORIENTATION#
Characterization of the orientation of the defect: |
“CIRC “for a circumferential defect, |
“LONGI “for a longitudinal defect. |
3.7. Keyword K1D#
Keyword factor for characterizing the thermomechanical transient. The repetition of this keyword is possible.
3.7.1. Operands TABL_MECA_REVet TABL_MECA_MDB#
Shape defect “ELLIPSE” with negative offset:
For this type of defect, the two tables TABL_MECA_REVet TABL_MECA_MDB are mandatory, they provide the transient of the stresses experienced by the tank during the history of the loading, respectively on the coating side (from the point A of the defect to the interface) and on the base metal side (from the interface to the point B of the defect).
Shape defect “ELLIPSE” with positive offset:
For this type of defect, table TABL_MECA_MDB is mandatory, it provides the transient of the stresses experienced by the tank during the history of loading, respectively on the coating side (from point A of the defect) and on the base metal side (at point B of the defect) and on the base metal side (at point B of the defect).
Shape defect “SEMI_ELLIPSE” :
For this type of defect, table TABL_MECA_MDB is mandatory, it provides the transient of the stresses experienced by the tank during the history of the loading, respectively on the coating side (from point A of the defect: interface between the coating and the base metal) and on the base metal side (at point B of the defect).
The common parameters required for these tables are:
“INST” [R],
“SIXX” [R] (in 3D with “LONGI”),
“SIYY” [R] (in 3D with “LONGI” or in 2D with “CIRC”),
“SIXY” [R] (in 3D with “LONGI”),
“SIZZ” [R] (in 2D with “LONGI” or in 3D with “CIRC”).
The required parameters specific to:
TABL_MECA_REVsont:
“COOR_X” [R],
“COOR_Y” [R]
TABL_MECA_MDBsont:
“ABSC_CURV” [R]
The reader is invited to consult the documentation for commands POST_RELEVE_T [U4.81.21] and MACR_LIGN_COUPE [U4.81,13] for more information on the meaning of the parameters.
In the case of a form defect “SEMI_ELLIPSE” the macro command MACR_LIGN_COUPE must be used with the keywords TYPE =” SEGMENT “and NB_POINTS =5. The influence coefficient method requires the evaluation of a degree 5 polynomial representing the evolution of the stress normal to the segment representing the crack [R7.02.10]. The macro command MACR_LIGN_COUPE allows the user to define the places where the stress is detected and this is independent of the mesh used during the thermo-mechanical study.
3.7.2. Operand TABL_THER#
Table providing the thermal transient in the tank during the history of loading from tip A to tip B.
The required parameters of this table are:
“INST” [R],
“ABSC_CURV” [R],
“TEMP” [R].
The reader is invited to consult the documentation for commands POST_RELEVE_T [U4.81.21] and MACR_LIGN_COUPE [U4.81.13] for more information on the meaning of the parameters.
3.7.3. Operand INTITULE#
Title to specify the group of nodes in question.
3.8. Operand TITRE#
Title attached to the concept produced by this operand [U4.03.01].