1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
It is a cube with 8 nodes, where three faces have a zero normal displacement and the three opposite faces have an imposed and identical normal displacement.
The cube has a side length of \(1\mathit{mm}\). In modeling A, the cube is oriented according to the coordinate system \(\mathit{Oxyz}\).
Modeling A
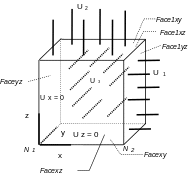
\({U}_{2}\mathrm{=}{U}_{1}\mathrm{=}{U}_{3}\)
1.2. Material properties#
To test the irreversible evolution of mechanical characteristics with temperature, a decreasing temperature field is applied. Some variables depend on temperature, others on drying. Finally, a non-zero desiccation shrinkage coefficient, equal to the thermal expansion coefficient, is applied to test « computer » operation. The thermal deformations will thus be equal and opposite to the deformations due to desiccation shrinkage. These dependencies only occur for purely computer checks; the mechanical characteristics can be considered to be constant.
For the usual linear mechanical characteristics:
Young’s module: |
\(E\mathrm{=}32000\mathit{MPa}\) |
from |
\(0°C\) to \(20°C\) |
\(E\mathrm{=}15000\mathit{MPa}\) |
to |
\(400°C\) (linear decay) |
|
\(E\mathrm{=}5000\mathit{MPa}\) |
to |
\(800°C\) (linear decay) |
|
Poisson’s ratio: |
\(\nu \mathrm{=}0.18\) |
||
Thermal expansion coefficient: |
\(a\mathrm{=}{10}^{\mathrm{-}5}\mathrm{/}°C\) |
||
Desiccation shrinkage coefficient: |
\(k\mathrm{=}{10}^{\mathrm{-}5}\) |
For the non-linear mechanical characteristics of the model **** BETON_DOUBLE_DP :**
Uniaxial compression strength: |
\(f\text{'}c\mathrm{=}40N\mathrm{/}{\mathit{mm}}^{2}\) |
of |
\(0°C\) to \(400°C\) |
\(f\text{'}c\mathrm{=}15N\mathrm{/}{\mathit{mm}}^{2}\) |
unto |
\(800°C\) (linear decay) |
|
Uniaxial tensile strength: |
\(f\text{'}t\mathrm{=}4N\mathrm{/}{\mathit{mm}}^{2}\) |
of |
\(0°C\) to \(400°C\) |
\(f\text{'}t\mathrm{=}1.5N\mathrm{/}{\mathit{mm}}^{2}\) |
unto |
\(800°C\) (linear decay) |
|
Compressive strength ratio |
|||
biaxial/uniaxial compression: |
\(b\mathrm{=}1.16\) |
||
Breakdown energy in compression: |
\({G}_{c}\mathrm{=}10\mathit{Nmm}\mathrm{/}{\mathit{mm}}^{2}\) |
||
Tensile break energy: |
\({G}_{t}\mathrm{=}0.1\mathit{Nmm}\mathrm{/}{\mathit{mm}}^{2}\) |
||
Ratio of the elastic limit to the strength |
|||
in uniaxial compression: |
30% |
||
1.3. Boundary conditions and mechanical loads#
Temperature field decreasing from \(20°C\) to \(0°C\). |
|
Underside of the cube (\(\mathit{facexy}\)): |
blocked next \(\mathit{oz}\). |
Top side of the cube (\(\mathit{face1xy}\)): |
Displacement \({U}_{z}\mathrm{=}\mathrm{0,15}\mathit{mm}\) |
Left side of the cube (\(\mathit{faceyz}\)): |
blocked next \(\mathit{ox}\). |
Right side of the cube (\(\mathit{face1yz}\)): |
Displacement \({U}_{x}\mathrm{=}\mathrm{0,15}\mathit{mm}\) |
Front side of the cube (\(\mathit{facexz}\)): |
blocked next \(\mathit{oy}\). |
Back side of the cube (\(\mathit{face1xz}\)): |
Displacement \({U}_{y}\mathrm{=}\mathrm{0,15}\mathit{mm}\) |