1. Reference problem#
1.1. Geometry#
The stresses and deformations are homogeneous in the volume element. This can be represented by a plane or a solid element, for example:
1.2. Material properties#
Law of elastoplastic behavior with linear kinematic work hardening.
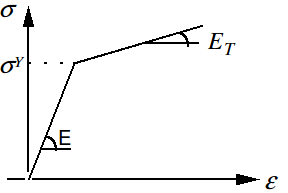
\(\begin{array}{c}E\mathrm{=}195000\mathit{MPa}\\ \nu \mathrm{=}0.3\\ {\sigma }^{Y}\mathrm{=}181\mathit{MPa}\\ {E}_{T}\mathrm{=}1930\mathit{MPa}\end{array}\)
1.3. Boundary conditions and loads#
The volume element is locked along \(\mathrm{Ox}\) along the \([\mathrm{2,4}]\) side while being subjected to a pull \({\sigma }^{D}\) and a shear force \({\tau }^{D}\).
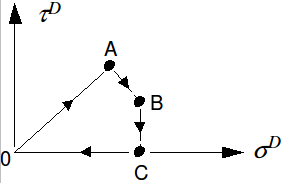
The loading path is as follows:
\({\sigma }^{D}\) |
\({\tau }^{D}\) |
|
(\(\mathit{MPa}\)) |
(\(\mathit{MPa}\)) |
|
\(A\) |
151.2 |
93.1 |
\(B\) |
257.3 |
33.1 |
\(C\) |
259.3 |
0 |