2. Reference solution#
2.1. Calculation method used for the reference solution#
Finite element calculation with Samcef Version 7.0 (Mecanl).
2.2. Reference solution#
Variation of tensions on the skin along the meridian section for internal pressure \({p}_{0}\) [bib2]
Variation of tensions on the skin along the meridian section in the vicinity of the ruin for internal pressure \({p}_{\mathrm{max}}\) [bib2]
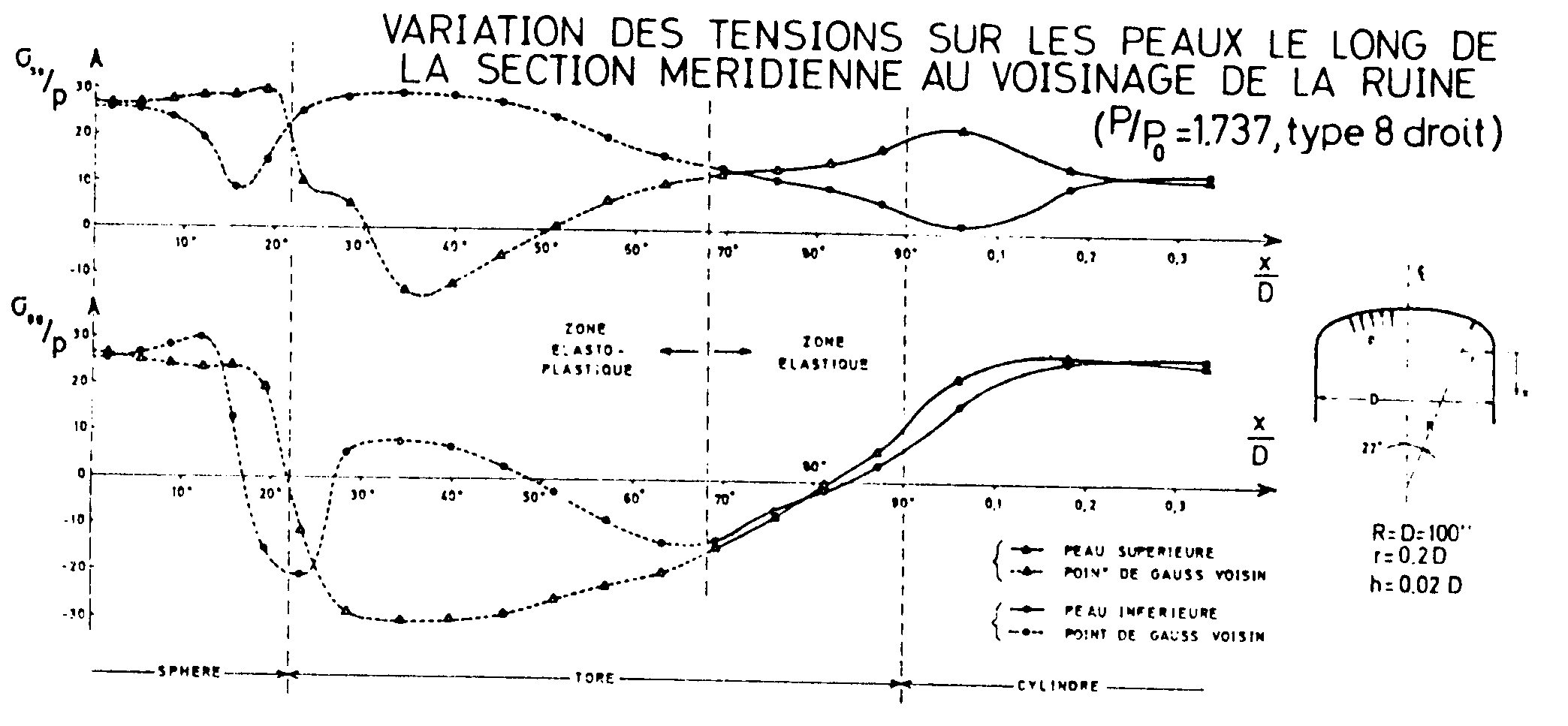
Variation in azimuthal stress \({\sigma }_{\theta \theta }\) on the upper skin along the meridian section in the vicinity of the ruin for internal pressure \({p}_{\mathrm{max}}\) . Geometric linear calculation.
Variation in azimuthal stress \({\sigma }_{\theta \theta }\) on the lower skin along the meridian section in the vicinity of the ruin for internal pressure \({p}_{\mathrm{max}}\) . Geometric linear calculation.
Variation in azimuthal stress \({\sigma }_{\theta \theta }\) on the upper skin along the meridian section in the vicinity of the ruin for internal pressure \({p}_{\mathrm{max}}\) . Geometric nonlinear calculation.
Variation in azimuthal stress \({\sigma }_{\theta \theta }\) on the lower skin along the meridian section in the vicinity of the ruin for internal pressure \({p}_{\mathrm{max}}\) . Geometric nonlinear calculation.
Discretization used for the reference solution. Definition of axes
Geometric nonlinear calculation: \(\mathrm{pression}={p}_{\mathrm{max}}\)
Geometric linear calculation: \(\mathrm{pression}={p}_{\mathrm{max}}\)
Skin |
Meridian length
|
Knot position |
|
0.0 |
1 |
26.2 |
|
Superior |
45.1 |
71 |
—30.7 |
138 |
137 |
24.0 |
|
0.0 |
1 |
25.231 |
|
22.833 |
37 |
29.899 |
|
Inferior |
32.981 |
53 |
—16.127 |
52.707 |
87 |
—13,756 |
|
134.76 |
137 |
25.008 |
Movement field (point \(A\) , lower skin)
Calculus… geometric |
Meridian length \((\mathrm{inch})\) |
Node position |
Pressure |
Displacement \({U}^{Z}\) \((\mathrm{inch})\) |
|
Linear |
0.0 |
1 |
|
0.100945 |
|
0.0 |
1 |
|
0.370468 |
||
Nonlinear |
0.0 |
1 |
1 |
|
0.0990524 |
0.0 |
1 |
|
0.244347 |
2.3. Uncertainty about the solution#
Uncertainty less than \(\text{2 \%}\) (linear regime), less than \(\text{5 \%}\) (elasto-plastic regime).
2.4. Bibliographical references#
LARSEN, P.K., POPOV, E.P., E.P., Elastic-plastic analysis of thick-walled pressure vessels with sharp discontinuities, Trans. ASME Applied Mechanics, pp 1016-1019, 1971
NYSSEN, C., Finite element modeling of the nonlinear behavior of aerospace structures, doctoral thesis, University of Liège, 1979