2. Benchmark solution#
2.1. Calculation method used for the reference solution#
The reference solution is taken from [1]. It is a finite element calculation with a penalization method and an explicit time diagram of centered difference. The mesh size and the result of the reference calculation are shown below.
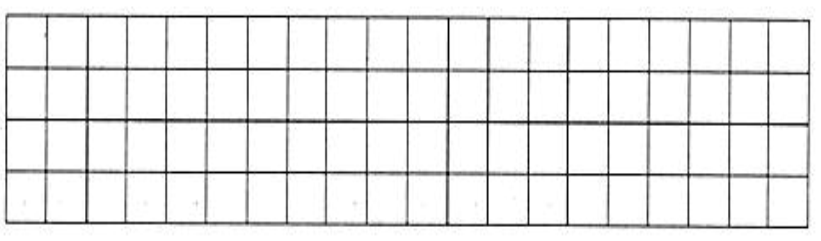
Figure: Finite element mesh from the reference calculation (Extracted from [1]).
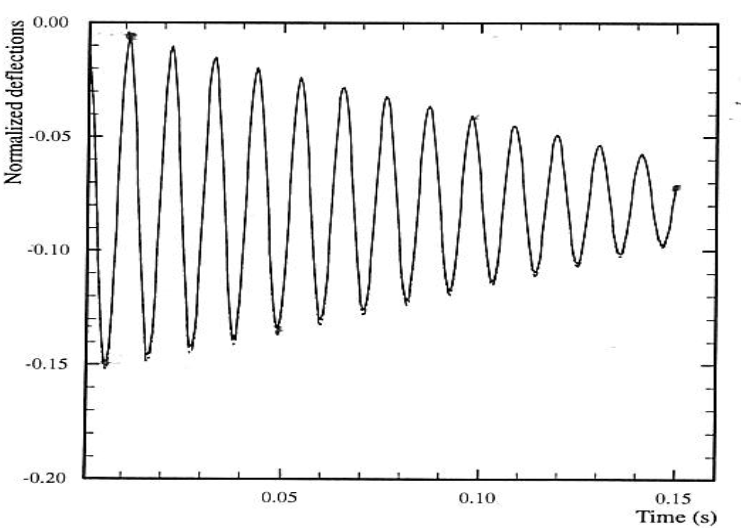
Figure: Vertical displacement solution of the reference calculation (Excerpted from [1]).
It can be clearly seen that the solution is amortized over time. Damping is strongly linked to connection parameters (impact, friction, reactions to supports)
2.2. Uncertainty about the solution#
Since all the numerical parameters of the reference solution are not known, differences between solution SOURCE_EXTERNE and the code solution can be expected. Instead, we will focus on orders of magnitude.
In some models, the aim is to compare the results of different algorithms and schemes. To do this, we do the same calculation with DYNA_NON_LINE by only changing the definition of the contact according to the algorithm or the definition of the diagram in time. Then, starting with CREA_CHAMP, we create a EVOL_NOLI structure representing the difference in results between two algorithms/schemes. Finally, we test whether the results of the two algorithms/schemes are the same in one node.
2.3. References#
[1] Zhi-Hua Zong, Finite element procedures for Contact-Impact problems, Oxford Science Publication, p162.