1. Reference problem#
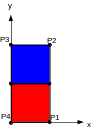
1.1. Geometry#
Axisymmetric cylinder
1.2. Material properties#
The material properties of the two sub-domains (blue and red) are those of 316L steel, described below. Work hardening restoration parameters are also defined but only on the red subdomain.
Thermal parameters:
Volume heat capacity \(\rho {C}_{p}=3.9\times {10}^{6}({\mathit{J.m}}^{-3.}°{C}^{-1})\)
Conductivity \(\lambda ({\mathit{W.m}}^{-1}°{C}^{-1})\):
T (°C) |
\(\lambda\) |
15.2 |
|
16.6 |
|
17.9 |
|
19.0 |
|
20.6 |
|
21.8 |
|
23.1 |
|
24.3 |
|
27.3 |
|
29.9 |
|
Thermo-mechanical parameters:
Thermo-elastic parameters:
Young’s module \(E(\mathit{Pa})\)
Poisson’s ratio: \(\nu =0.3\)
Thermal expansion coefficient \(\alpha\)
Expansion coefficient definition temperature: \({T}_{\mathit{ref}}=20°C\)
Elasticity limit \({\sigma }_{y}(\mathit{Pa})\)
Thermoplastic parameters (law with linear work hardening)
Tangent module \({E}_{T}(\mathit{Pa})\)
T (°C) |
\({E}_{T}(\times {10}^{6})\) |
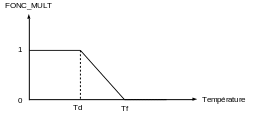
Work hardening restoration parameter: multiplicative function FONC_MULT
Restoration start temperature: Td = 600°C
Temperature at the end of restoration: Tf = 1000°C
1.3. Boundary conditions and loads#
Blockages:
uy = 0 in P1, P2, P3 and P4
Charging:
The following thermal load is applied all over the mesh:
with T0 = 20°C and T1 = 1125°C
