1. Description#
1.1. Geometry#
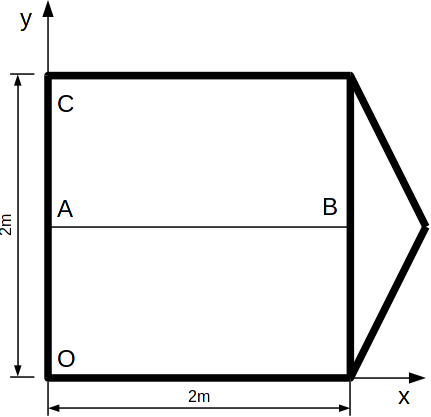
The concrete plate consists of a square with a side of \(2m\) and an isosceles triangle with a base of \(2m\) and a height of \(\mathrm{0,5}m\).
The thickness of the plate is \(e\mathrm{=}\mathrm{0,6}m\).
A cable, located on segment \(\mathrm{[}\mathit{AB}\mathrm{]}\), crosses the square part of the plate horizontally, halfway up, without eccentricity in the thickness. The cross-sectional area of the cable is \({S}_{a}\mathrm{=}\mathrm{1,5}{.10}^{\mathrm{-}4}{m}^{2}\).
1.2. Material properties#
The plate is made of concrete and the cable is made of steel.
Material |
Concrete |
Steel |
Young’s module |
\({E}_{b}\mathrm{=}{3.0}^{10}\mathit{Pa}\) |
|
Poisson’s ratio |
\({\nu }_{b}\mathrm{=}0.3\) |
|
Density |
\({m}_{b}\mathrm{=}2500\mathit{Kg}\mathrm{/}{m}^{3}\) |
|
1.3. Boundary conditions#
Nodes \(O\) and \(C\) are embedded: all degrees of freedom of translation and rotation are locked.